fume hood → digestor
Fume hood is a type of local exhaust ventilation system (engineering control). A typical fume hood is cabinet with a moveable front sash (window) made out of safety glass. Air is drawn into the hood under and through the opened sash and is exhausted through openings in the rear and top of the cabinet to a remote point such as an exhaust stack on the roof of the building. A properly used and properly functioning fume hood exhausts hazardous gases, dusts, mists, and vapors from a confined location and helps protect workers from inhalation exposure.
gas → plin
Gas is a state of matter, in which the mollecules move freely and consequently the entire mass tends to expand indefinitely, occupying the total volume of any vessel into which it is introduced. Gases follow, within considerable degree of fidelity, certain laws relating their conditions of pressure, volume and temperature. Gases mix freely with each other, and they can be liquefied through compression or temperature reduction.
gas washing bottle → boca ispiralica
Gas washing bottle or Drechsel bottle provide an inexpensive but effective method for washing or drying gases. The gas enters the bottle through the top of the central vertical tube, the lower end of which is below the surface of the washing medium. To maximize surface area contact of the gas to the liquid, a gas stream is slowly blown into the vessel through the fritted glass tip so that it breaks up the gas into many tiny bubbles. After bubbling through the medium, the gas rises to the top and exits through the side tube. It is named after the German chemist Edmund Drechsel (1843-1897).
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
glass electrode → staklena elektroda
Glass electrode is a hydrogen-ion responsive electrode usually consisting of a bulb, or other suitable form, of special glass attached to a stem of high resistance glass complete with internal reference electrode and internal filling solution system. Glass electrode is also available for the measurement of sodium ions.
The glass electrode, which consists of a thin wall glass bulb, has an extremely high electrical resistance. The membrane of a typical glass electrode (with a thickness of 0.03 mm to 0.1 mm) has an electrical resistance of 30 MΩ to 600 MΩ. The surface of a glass membrane must be hydrated before it will function as a pH electrode. When a glass surface is immersed in an aqueous solution then a thin solvated layer (gel layer) is formed on the glass surface in which the glass structure is softer. This applies to both the outside and inside of the glass membrane.
The simplest explanation for the working of the thin glass electrode is that the glass acts as a weak acid (Glass-H).
The hydrogen ion activity of the internal solution is held constant. When a solution of different pH from the inside comes in contact with the outside of the glass membrane, the glass is either deprotonated or protonated relative to the inside of the glass. The difference in pH between solutions inside and outside the thin glass membrane creates electromotive force in proportion to this difference in pH.
global warming → globalno zatopljenje
Global warming or greenhouse effect is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of certain gases (greenhouse gases) that absorb infrared radiation. Light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun is able to penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. This energy is re-radiated as infrared radiation which because of its longer wavelength, is absorbed by such substances as carbon dioxide. The overall effect is that the average temperature of the Earth and its atmosphere is increasing (so-called global Warming). The effect is similar to that occurring in a greenhouse, where light and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation can pass through the glass into greenhouse but the infrared radiation is absorbed by the glass and part of it is re-radiated into the greenhouse.
The greenhouse effect is seen as a major environmental hazard. Average increases in temperature could change weather patterns and agricultural output. It might also lead to melting of the polar ice caps and a corresponding rise in sea level. Carbon dioxide, from fossil-fuel power stations and car exhausts, is the main greenhouse gas. Other contributory pollutants are nitrogen oxides, ozone, methane, and chloroflourocarbons.
glutamine → glutamin
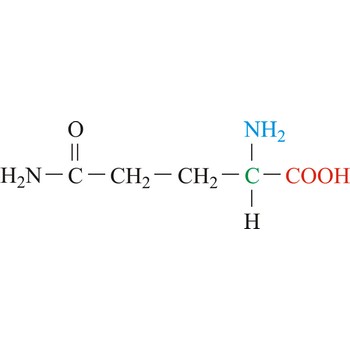
Glutamine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It serves as an important carrier of ammonia and contributes it to the formation of urea and purines. Glutamine is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia.
- Abbreviations: Gln, Q
- IUPAC name: 2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular weight: 146.14 g/mol
glycine → glicin
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and is unique because it lacks a side chain. This gives it more conformational freedom than any other amino acid. Glycine is often found in turns and loops where other amino acids would be sterically unacceptable. Although it is formally nonpolar, it’s very small side chain makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions. Glycine is not essential to the human diet, as it is biosynthesized in the body from the amino acid serine.
- Abbreviations: Gly, G
- IUPAC name: 2-aminoacetic acid
- Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular weight: 75.07 g/mol
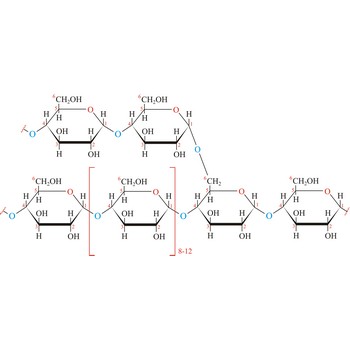
glycogen → glikogen
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Gallery/images.php." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table