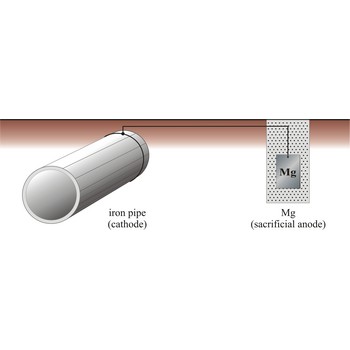
cathodic protection → katodna zaštita
Cathodic protection is a process in which a structural metal, such as iron, is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a metal that has a more negative reduction half-cell potential, which now corrodes instead of iron. There are two major variations of the cathodic method of corrosion protection. The first is called the impressed current method, and the other is called the sacrificial anode method.
Faradaic reaction → Faradejska reakcija
Faradaic reaction is a heterogeneous charge-transfer reaction occurring at the surface of an electrode.
irreversible galvanic cell → nepovrativi galvanski članak
Irreversible galvanic cell is a chemical source of direct current, in which reactions that take place on the electrodes are irreversible.
ohm → om
Ohm (Ω) is the SI derived unit of electric resistance. The ohm is the electric resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant difference of potential of one volt, applied between these two points, produces in this conductor a current of one ampere, this conductor not being the source of electromotive force (Ω = V/A). The unit was named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1789-1854).
Daniell cell → Daniellov članak
In 1836 the British chemist John Frederic Daniell (1790-1845) proposed an improved electric cell that supplied an even current during continuous operation. Daniell cell consisted of a glass jar containing copper and zinc electrodes, each immersed in their respective acidic sulphate solutions. The two solutions were separated by a porous clay cylinder separator. It was a galvanic cell in which the spontaneous electrodissolution of zinc and electroplating of copper provided the electrical current.
Zn(s) |
→ | Zn2+ + 2e- |
+0.763 V |
Cu2+ + 2e- |
→ | Cu(s) |
+0.337 V |
Zn(s) + Cu2+ |
→← | Zn2+ + Cu(s) |
+1.100 V |
reaction layer → reakcijski sloj
Reaction layer (in electrochemistry) is that layer of solution adjacent to an electrode within which a stationary distribution of electroactive species is established as the result of homogeneous reaction.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Electrode potential series." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table