cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
cysteine → cistein
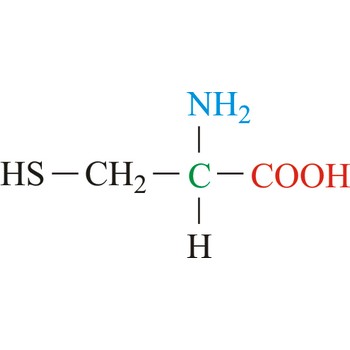
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
Markovnikov’s rule → Markovnikovljevo pravilo
Markovnikov’s rule: when an asymmetrical alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide to give an alkyl halide, the hydrogen adds to the carbon of the alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer number of hydrogen substituents.
decomposition → raspadanje
Decomposition occurs when chemical compounds are broken up into simple molecules, and even as far as their original elements. These processes are normally irreversible. An example of decomposition is when ammonium nitrate is heated. This produces nitrous oxide and water which are unable to recombine.
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
diffusion → difuzija
Diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of one substance with another when in contact or separated by a permeable membrane. Diffusion is a result of the random motions of their component atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles. Diffusion occurs most readily in gases, less so in liquids, and least in solids. The rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration of the substance and increases with temperature. The theoretical principles are stated in Fick’s laws.
mean free path → srednji slobodni put
Mean free path is the average distance a gas molecule travels between collisions.
metabolism → metabolizam
Metabolism is a sum of all chemical and physiological processes by which the body builds and maintains itself. It is a process of building the body’s molecular structures from nutrients (anabolism) and breaking them down for energy (catabolism).
micelle → micele
Micelle is an electrically charged colloidal particle, usually organic in nature, composed of aggregates of large molecules, e.g., in soaps and surfactants. For aqueous solutions, the hydrophilic end of the molecule is on the surface of the micelle, while the hydrophobic end (often a hydrocarbon chain) points toward the centre.
disaccharide → disaharid
Disaccharides are compounds in which two monosaccharides are joined by a glycosidic bond. A glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon can be either α or β. For example, maltose, the disaccharide obtained by enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of starch, consists of two D-glucopyranose units joined by a 1,4’-α-glycoside bond. The "prime" superscript indicates that C-4 is not in the same ring as C-1. Unlike the other disaccharides, sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation because the glycosidic bond is between the anomeric carbon of glucose and the anomeric carbon of fructose.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Dipolna molekula." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table