saturated fatty acid → zasićena masna kiselina
Saturated fatty acid is a fatty acid carrying the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms (It doesn’t have any double bounds in the alkyl chain). The most important of these are:
| Butyric (butanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)2COOH |
| Lauric (dodecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)10COOH |
| Myristic (tetradecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)12COOH |
| Palmitic (hexadecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)14COOH |
| Stearic (octadecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)16COOH |
| Arachidic (eicosanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)18COOH |
unsaturated fatty acid → nezasićena masna kiselina
Unsaturated fatty acid is a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms. Their carbon chain has one or more double or triple valence bond per molecule. The most important of these are:
| Oleic (9-octadecenoic acid) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
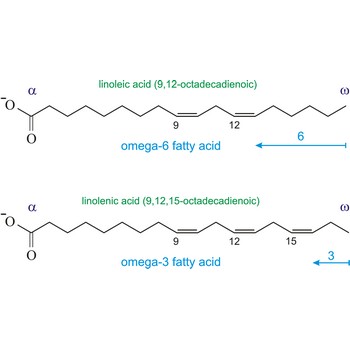
| Linoleic (9,12-octadecadienoic acid) | CH3(CHCH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CHCH2)7COOH |
| Linolenic (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid) | CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CHCH2)7COOH |
acid dissociation constant → konstanta disocijacije kiseline
Acid dissociation constant (Ka) is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid HA through the reaction
The quantity pKa = -log Ka is often used to express the acid dissociation constant.
carboxylic acids → karboksilne kiseline
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more RC(=O)OH groups (the carboxyl group). In the systematic chemical nomenclature carboxylic acids names end in the suffix -oic (e.g. ethanoic acids, CH3COOH). The carbon of the terminal group being counted as part of the chain. They are generally weak acids. Carboxylic acids include a large and important class of fatty acids and may be either saturated or unsaturated. There are also some natural aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic, salicylic).
omega-3 fatty acids → omega-3 masne kiseline
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning they contain more than one double bond. The name omega-3 indicates that the first double bond occurs on the third carbon atom (n-3) from the methyl (-CH3) end of the molecule (omega position). The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3). ALA comes from plants. EPA and DHA come from fish.
Similarly, the first double bond in omega-6 fatty acids is located between the sixth and seventh carbon atom (n-6) from the methyl end of the fatty acid (omega end).
polyprotonic acids → poliprotonske kiseline
Polyprotonic acids are acids which dissolve in more than one degree.
asparagine → asparagin
Asparagine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. The polar amino acids are an important class of amino acids since they provide many of the functional groups found in proteins. Asparagine is a common site for attachment of carbohydrates in glycoproteins. In general this is not very reactive residues. Asparagine is amide derivative of aspartic acid. Asparagine is not essential for humans, which means that it can be synthesized from central metabolic pathway intermediates and is not required in the diet.
- Abbreviations: Asn, N
- IUPAC name: 2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H8N2O3
- Molecular weight: 132.12 g/mol
acid halide → kiselinski halogenid
Acid halide is organic compound containing the group -COX where X is a halogen atom.
acid radical → kiseli radikal
Acid radical is an anion left after removal of hydrogen atoms from an acid.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Asparaginska kiselina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table