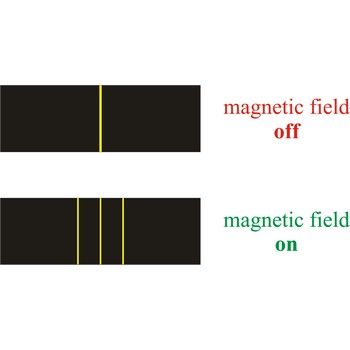
Zeeman effect is the splitting of the lines in a spectrum when the source of the spectrum is exposed to a magnetic field. The effect was discovered in 1896 by the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman (1865-1943) as a broadening of the yellow D-lines of sodium in a flame held between strong magnetic poles.
The Zeeman effect has helped physicists determine the energy levels in atoms. In astronomy, the Zeeman effect is used in measuring the magnetic field of the Sun and of other stars.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zeeman effect." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table
Find in dictionary:
Copyright © 2004-2023 by Eni Generalic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer