Results 1–3 of 3 for T-oblik geometrije molekule
biogas → bioplin
Biogas is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide resulting from the anaerobic decomposition of such waste materials as domestic, industrial, and agricultural sewage. Methanogenic bacteria carry out the decomposition; these obligate anaerobes produce methane, the main component of biogas, which can be collected and used as an energy source for domestic processes, such as heating, cooking, and lighting.
monoclinic crystal system → monoklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the monoclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes. Two of these axes (a and c) are inclined toward each other at an oblique angle; these are usually depicted vertically. The third axis (b) is perpendicular to the other two and is called the ortho axis. The two vertical axes therefore do not intersect one another at right angles, although both are perpendicular to the horizontal axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = γ = 90° ≠ β
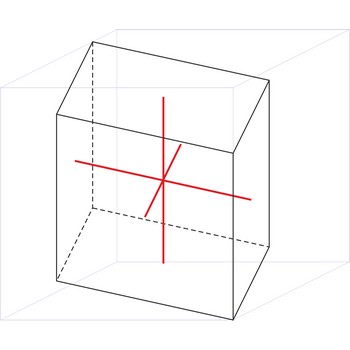
triclinic crystal system → triklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the triclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes, all of which intersect at oblique angles. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "T-oblik geometrije molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table