Hirsch funnel → Hirschov lijevak
Hirsch funnels are essentially smaller Büchner funnels and primarily used to collect a desired solid from a relatively small volume of liquid (1-10 mL). The main difference is that the plate is much smaller, while the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical. It is named after the German chemist Robert Hirsch (1856-1913).
Buchner funnel → Buchnerov lijevak
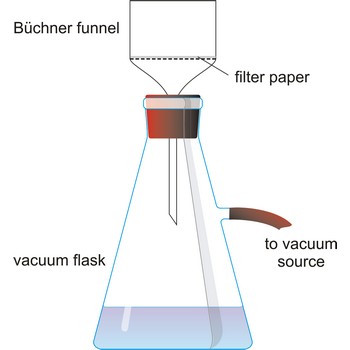
Büchner funnel is one device used for pressure assisted filtration. Buchner funnel is a cylindrical porcelain filtering funnel (glass and plastic funnels are also available) that has a perforated plate on which the flat filter paper is placed. A vacuum in the flask underneath the filter allows atmospheric pressure on the sample to force the liquid through the filter paper. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Wilhelm Büchner (1850-1925) who designed this funnel in 1885.
Bessemer, Henry → Bessemer, Henry
Sir Henry Bessemer (1813-1898) is the British engineer who first introduced a process for converting pig iron from a blast furnace into steel
bronze → bronca
Bronze is an alloy made primarily of copper and tin. It may contain as much as 25 % tin. Bronzes with 10 % or more tin are harder, stronger, and resistant to corrosion. As bronze weathers, a brown or green film forms on the surface. This film inhibits corrosion. Silicon or aluminium is often added to bronze to improve resistance to corrosion. Phosphorus, lead, zinc, and other metals may be added for special purposes. The alloy is hard and easily cast and is extensively used in bearings, valves and other machine parts.
Bronze was one of the first alloys developed by ancient metal workers. The Bronze Age occurred in Europe around 2200 to 700 BC. Bronze was used for weapons such as spearheads, swords, and knives. Since ancient times, bronze has been the most popular metal for casting statues and other art objects.

The term bronze has been adopted commercially for many copper-rich alloys that contain little or no tin but are similar in colour to bronze, including aluminium bronze, manganese bronze, and silicon bronze. Aluminium bronze is used to make tools and, because it will not spark when struck. Manganese bronze is actually a brass that contains manganese. It is often used to make ship propellers because it is strong and resists corrosion by sea water.
electrode potential → elektrodni potencijal
Electrode potential is defined as the potential of a cell consisting of the electrode in question acting as a cathode and the standard hydrogen electrode acting as an anode. Reduction always takes place at the cathode, and oxidation at the anode. According to the IUPAC convention, the term electrode potential is reserved exclusively to describe half-reactions written as reductions. The sign of the half-cell in question determines the sign of an electrode potential when it is coupled to a standard hydrogen electrode.
Electrode potential is defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen half cell
The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example
The e.m.f. of this cell is
By convention, at p(H2) = 101325 Pa and a(H+) = 1.00, the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is 0.000 V at all temperatures. As a consequence of this definition, any potential developed in a galvanic cell consisting of a standard hydrogen electrode and some other electrode is attributed entirely to the other electrode
extraction → ekstrakcija
Extraction is the separation of a component from its mixture by selective solubility. When a solution of one substance in one solvent is brought in with another solvent dissolved substance will distribute between the two solutants because of different solubility. Extraction is an efficient and fast method used for separating and concentrating matters. Extraction is best done several times in a succession, with smaller amount of solvent in it the matter is better dissolved. For example, caffeine can be separated from coffee beans by washing the beans with supercritical fluid carbon dioxide; the caffeine dissolves in the carbon dioxide, but flavour compounds do not. Vanillin can be extracted from vanilla beans by shaking the beans with an organic solvent, like ethanol.
filter flask → boca za odsisavanje
Filter flask, also known as a vacuum flask, is a flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied. It usually have heavy side walls to withstand high vacuum.
hardness → tvrdoća
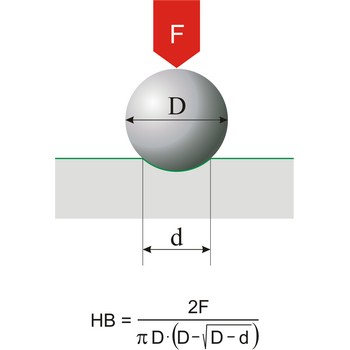
Hardness is the resistance of a material to deformation of an indenter of specific size and shape under a known load. This definition applies to all types of hardness scales except Mohs scale, which is a based on the concept of scratch hardness and is used chiefly for minerals. The most generally used hardness scales are Brinell (for cast iron), Rockwell (for sheet metal and heat-treated steel), Knoop (for metals).
Kjeldahl’s method → Kjeldahlov postupak
Kjeldahl’s method is an analytical method for determination of nitrogen in certain organic compounds. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
It involves addition of a small amount of anhydrous potassium sulphate to the test compound, followed by heating the mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid, often with a catalyst such as copper sulphate. As a result ammonia is formed. After alkalyzing the mixture with sodium hydroxyde, the ammonia is separated by distillation, collected in standard acid, and the nitrogen determined by back-titration.
- Kjeldahl flask for decomposition (500 ml – macro or 100 ml - micro)
- funnel for alkaline solution
- Wagner tube (drop catcher)
- condenser
- absorption flask with known volume of standard acid
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hirschov lijevak." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table