Knudsen burette → Knudsenova bireta
Knudsen's automatic bulb-burette, developed by the Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949), is designed in a way that even routine field analysis in a boat laboratory would provide highly accurate measurements. The burette is filled with a mixture of silver nitrate from reservoir R, located above the burette, by opening the A valve. When the solution crosses the three-way C valve the A valve is closed preventing further solution flow in to the burette. Any extra solution is caught in the W bowl. Turn the C valve, which marks the zero on the scale, in order to allow atmospheric air to enter the burette. Since most open-ocean samples lie in a relatively small chlorinity range, the burette is designed so that much of its capacity is in the bulb (B). This allows the titration to be quick (by quickly releasing contents from the B area) and reduces the error that occurs from the slow drainage along the inner wall of the burette.
Each millimeter is divided in to twenty parts (double millimeter division of the Knudsen burette) which allows for highly accurate measurements (the scale is read up to a precision of 0.005 mL). From 0 to 16 the burette isn't divided, that usually starts from 16 and goes until 20.5 or 21.5. A single double millimeter on a Knudsen burette scale corresponds to one permille of chloride in the seawater sample. This burette can be used for titration of water from all of the oceans and seas, with the exemptions being areas with very low salinity (e.g. the Baltic Sea) and river estuaries which require the use of normal burettes.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
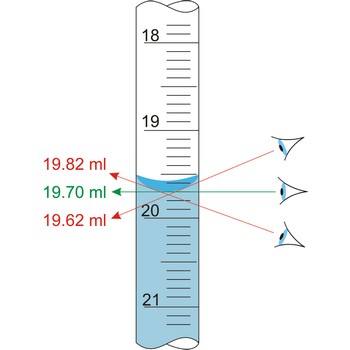
parallax → paralaksa
Parallax is a deceptive change of the position of an object which is observed while the position of the observer changes. Position of eye at all volumetric vessels must be at the same level as the meniscus. If not, the parallax will cause an error while reading the position of the meniscus of a liquid in a burette. It will be a positive mistake if the eye is lower, and negative if the eye is higher than the meniscus plane.
Petri dish → Petrijeva zdjelica
Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic flat bottomed dish with a lid. Used primarily in laboratories for the culture of bacteria and other microorganisms on specially prepared media. It was named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri (1852-1921) who invented it in 1877.
polonium → polonij
Polonium was discovered by Marie Curie (Poland) in 1898. Named for Poland, native country of Marie Curie. It is silvery-grey, extremely rare, radioactive metal. Soluble in dilute acids. Highly toxic. Severe radiotoxicity. Carcinogen. Polonium occurs in pitchblende. Produced by bombarding bismuth with neutrons. Used in industrial equipment that eliminates static electricity caused by such processes as rolling paper, wire and sheet metal.
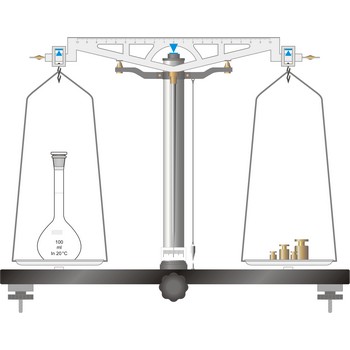
precision balance → tehnička vaga
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
salt bridge → solni most
Salt bridge is a permeable material soaked in a salt solution that allows ions to be transferred from one container to another. The salt solution remains unchanged during this transfer.
silver → srebro
Silver has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word argentum meaning silver. It is silvery-ductile and malleable metal. Stable in water and oxygen. Reacts with sulfur compounds to form black sulfides. Silver is found in ores called argentite (AgS), light ruby silver (Ag3AsS3), dark ruby silver (Ag3SbS3) and brittle silver. Used in alloys for jewellery and in other compounds for photography. It is also a good conductor, but expensive.
silver coulometer → srebrni kulometar
Silver coulometer consists of a platinum vessel which acts as a cathode and contains a solution of pure silver nitrate as an electrolyte (c(AgNO3) = 1 mol/L). A rod of pure silver enclosed in a porous pot acts as the anode. The current density at the anode should not exceed 0.2 Acm-2. After electrolysis, the electrolyte is taken out and the platinum vessel is washed, dried and weighed. The increase in the weight gives the amount of silver deposited (96500 C of electricity deposits 107.88 g of silver). From the mass of the silver deposited, the coulomb involved in the reaction can be calculated.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Dewarova posuda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table