ampere → amper
Ampere (A) is the SI base unit of electric current.
The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 metre apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2×10-7 newton per metre of length.
amphoteric substances → amfoterna tvar
Amphoteric substances can behave as acids or as bases depending upon their surroundings. So aluminium hydroxide in reaction with acids will behave as a base
and in reaction with bases it will act as an acid
AMU → AMU
AMU or atomic mass unit is a unit of mass used to express relative atomic masses. It is equal to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of the isotope carbon-12 and is equal to 1.66 033×10-27 kg. This unit superseded both the physical and a chemical mass unit based on oxygen-16 and is sometimes called the unified mass unit or the dalton.
anion exchange → anionski izmjenjivač
An anionic resin has negative ions built into its structure and therefore exchanges positive ions. In an anion exchange, the side groups are ionised basic groups, such as (-NH2, -NRH, -NR2, -NR3+) to which anions OH- are attached. The exchange reaction is one in which different anions in the solution displace the OH- from the solid.
atomic clock → atomski sat
Atomic clock is an apparatus for standardizing time based on periodic phenomena within atoms or molecules (ammonia clock; caesium clock).
analytical balance → analitička vaga
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
anomer → anomer
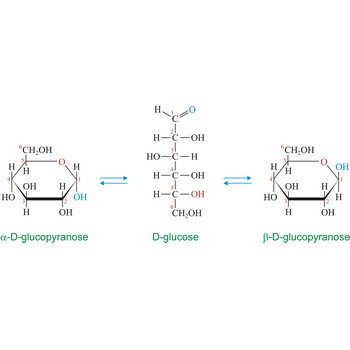
Anomers are diastereoisomers of cyclic forms of sugars or similar molecules differing in the configuration at the anomeric carbon (C-1 atom of an aldose or the C-2 atom of a 2-ketose). The cyclic forms of carbohydrates can exist in two forms, α- and β- based on the position of the substituent at the anomeric center. Anomer are designated α if the configuration at the anomeric carbon is the same as that at the reference asymmetric carbon in a Fischer projection. If the configuration differs the anomer is designated β. For example, α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose, the two cyclic forms of glucose, are anomers.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Brösted base." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table