titrant → titrant
Titrant is the substance that quantitatively reacts with the analyte in a titration. The titrant is usually a standard solution added carefully to the analyte until the reaction is complete. The amount of analyte is calculated from the volume and concentration of titrant required for the complete reaction.
fuel cell → gorivi članak
Fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is different from a battery in that the energy conversion continues as long as fuel and oxidising agent are fed to the fuel cell; that is, in principle indefinitely. (A battery is manufactured with a limited amount of chemicals, and it is exhausted when all the chemicals have reacted.) It is a galvanic cell where spontaneous chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The fuel is oxidised at the anode, and the oxidising agent (almost always oxygen or air) is reduced at the cathode. Presently, the most commonly used fuel is hydrogen. More conventional fuels (e.g., petrol or natural gas) must be converted (reformed) into hydrogen before they can be utilised in a fuel cell.
Some fuel cells employ an aqueous solution as electrolyte, that can be either acidic or basic (alkaline), or an ion-exchange membrane soaked in aqueous solution can act as the electrolyte. These fuel cells operate at relatively low temperatures (from room temperature to not much above the boiling point of water). Some fuel cells employ molten salts (especially carbonates) as electrolytes and have to operate at temperatures of several hundred degrees centigrade (Celsius). Others employ ionically conductive solids as electrolyte and must operate close to 1 000 °C.
gold → zlato
Gold has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word aurum meaning gold. It is soft, malleable, bright yellow metal. Unaffected by air, water, alkalis and most acids. Gold is found in veins in the crust, with copper ore and native. Used in electronics, jewellery and coins. It is a good reflector of infrared radiation, so a thin film of gold is applied to the glass of skyscrapers to reduce internal heating from sunlight.
vapour pressure lowering → snižavanje tlaka pare
Vapour pressure is a colligative property of solutions. The vapour pressure of a solution is always lower than the vapour pressure of the pure solvent. Ratio of solution to pure solvent vapour pressures is approximately equal to the mole fraction of solvent in the solution.
weak acid → slaba kiselina
Weak acid is an acid that incompletely dissociated in aqueous solution. Acetic acid is an example of a weak acid
weak base → slaba baza
Weak base is a base that only partially dissociates into ions in solution. Weak bases are weak electrolytes. Ammonia is an example of a weak base
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
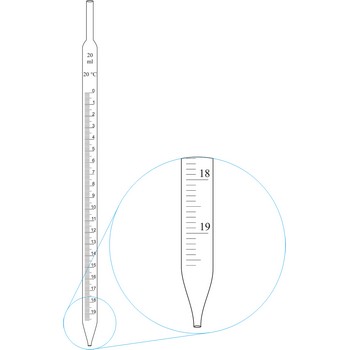
graduated pipette → graduirana pipeta
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark 0. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely.
weak electrolyte → slabi elektrolit
Weak electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions dissociate only partially, giving ions and which are in equilibrium with undissociated molecules. Their water solutions conduct electric current weakly. For example, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions, so that an acetic acid solution contains both molecules and ions.
Zimmermann-Reinhardt’s reagent → Zimmermann-Reinhardtov reagens
Zimmermann-Reinhardt’s reagent is a mixture of manganese(II) sulphate, sulphuric acid and phosphorus acid. It is used for preventing oxidation of chloride ion while titrating iron(II) ion with permanganate solution.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zasićena otopina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table