enthalpy → entalpija
Enthalpy (H) is a thermodynamic property of a system defined by
where U is the internal energy of the system, p its pressure, and V its volume. J.W. Gibbs put the concept of an ensemble forward in 1902. In a chemical reaction carried out in the atmosphere the pressure remains constant and the enthalpy of reaction (ΔH), is equal to
For an exothermic reaction ΔH is taken to be negative.
ether → eter
Ethers are organic compounds with a formula R-O-R, where R is not equal to H. They may be derived from alcohols by elimination of water, but the major method is catalytic hydration of olefins. They are volatile highly flammable compounds; when containing peroxides they can detonate on heating. The term ether is often used synonymously with diethyl ether.
experiment → eksperiment
Experiment is direct observation under controlled conditions. Most experiments involve carefully changing one variable and observing the effect on another variable (for example, changing temperature of a water sample and recording the change volume that results).
partial pressure → parcijalni tlak
Partial pressure is a pressure that one component of gas mixture would have if it were alone in the same volume and at the same temperature as the mixture is in now.
specific quantity → specifična veličina
Specific quantity is often convenient to express an extensive quantity (e.g., volume, enthalpy, heat capacity, etc.) as the actual value divided by mass. The resulting quantity is called specific volume, specific enthalpy, etc.
face-centered cubic lattice → plošno centrirana kubična rešetka
Face-centered cubic lattice (fcc or cubic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a =b =c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the fcc structures the spheres fill 74 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is four (8×1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4). There are 26 metals that have the fcc lattice.
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
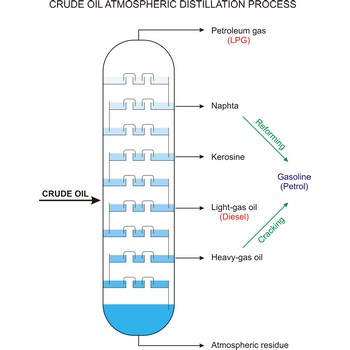
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
gas → plin
Gas is a state of matter, in which the mollecules move freely and consequently the entire mass tends to expand indefinitely, occupying the total volume of any vessel into which it is introduced. Gases follow, within considerable degree of fidelity, certain laws relating their conditions of pressure, volume and temperature. Gases mix freely with each other, and they can be liquefied through compression or temperature reduction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Volt." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table