atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
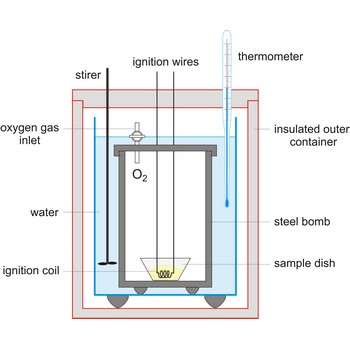
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
decomposition potential → potencijal razlaganja
Decomposition potential of some system is the smallest voltage which should be applied so that electrolysis occurs.
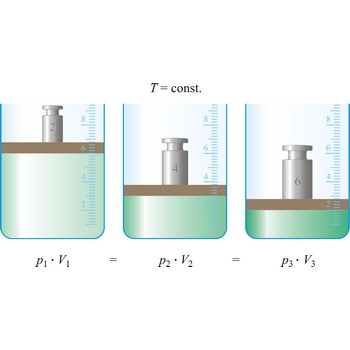
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
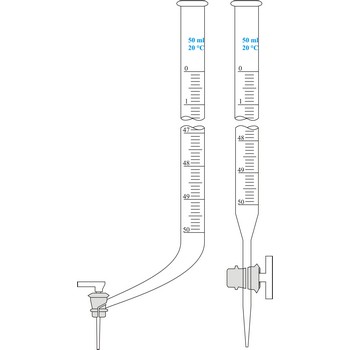
burette → bireta
Burette is a graded glass pipe which on its lower side has a glass faucet by which it can drop a precise quantity of liquid. Inner diameter of a burette must be equal in its whole length, because the accuracy of volume measurement depends upon that. Burettes are primarily used in volumetric analysis for titration with standard solution reagent. Most often Schellbach’s burette is used, graded on 50 mL with division of scale on 0.1 mL. Every burette is calibrated on discharge. For serial determining automatic burettes are used.
cetane number → cetanski broj
Cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of diesel fuel. It denotes the volume fraction of cetane (C16H34) in a combustible mixture (containing cetane and 1-methylnapthalene) whose ignition characteristics match those of the diesel fuel being tested. Cetane is a collection of un-branched open chain alkane molecule that ignites very easily under compression, so it was assigned a cetane number of 100, while alpha-methyl naphthalene was assigned a cetane number of 0.
equation of state → jednadžba stanja
Equation of state is an equation relating the pressure, volume, and temperature of a substance or system. Equation of state for ideal gas
where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
extensive property → ekstenzivno svojstvo
Extensive property is a property that changes when the amount of matter in a sample changes. Examples are mass, volume, length, and charge.
farad → farad
Farad (F) is the SI derived unit of electric capacitance. The farad is the capacitance of an electric capacitor between the two plates of which there appears a difference of electric potential of one volt when it is charged by a quantity of electricity equal to one coulomb (F = C/V). The unit was named after the British scientist M. Faraday (1791-1867).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Volt." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table