hydrogen → vodik
Hydrogen was discovered by Sir Henry Cavendish (England) in 1766. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words hydro and genes meaning water and generate. It is colourless, odourless gas, burns and forms explosive mixtures in air. Reacts violently with oxidants. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. Commercial quantities of hydrogen are produced by reacting superheated steam with methane or carbon. In lab work from reaction of metals with acid solutions or electrolysis. Most hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia and in metal refining. Also used as fuel in rockets. Its two heavier isotopes (deuterium and tritium) used respectively for nuclear fusion.
ionic conductor → ionski vodič
Ionic conductor is a material that conducts electricity with ions as charge carriers.
hydrogen bond → vodikova veza
Hydrogen is a bond formed by a hydrogen atom to an electronegative atom, and is denoted by dashed lines H-X---H-B. A hydrogen atom covalently bound to an oxygen (electronegative atom) has a significant positive charge and can form a weak bond to another electronegative atom.
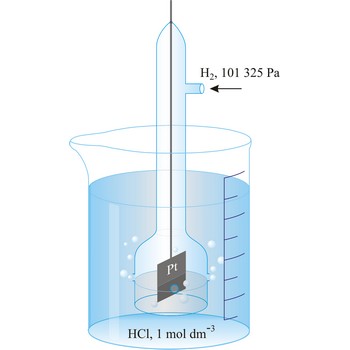
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
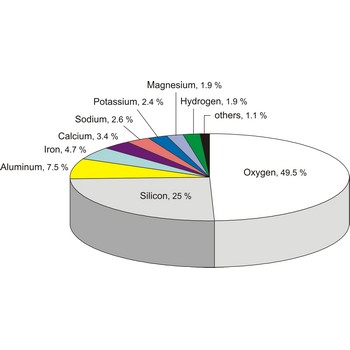
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
acid → kiselina
Acid is a type of compound that contains hydrogen and dissociates in water to produce positive hydrogen ions. The reaction for an acid HA is commonly written:
In fact, the hydrogen ion (the proton) is solvated, and the complete reaction is:
This definition of acids comes from the Arrhenius theory. Such acids tend to be corrosive substances with a sharp taste, which turn litmus red and produce colour changes with other indicators. They are referred to as protonic acids and are classified into strong acids, which are almost completely dissociated in water, (e.g. sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid), and weak acids, which are only partially dissociated (e.g. acetic acid and hydrogen sulphide). The strength of an acid depends on the extent to which it dissociates, and is measured by its dissociation constant.
In the Lowry-Brønsted theory of acids and bases (1923), the definition was extended to one in which an acid is a proton donor (a Brønsted acid), and a base is a proton acceptor (a Brønsted base). An important feature of the Lowry-Brønsted concept is that when an acid gives up a proton, a conjugate base is formed that is capable of accepting a proton.
Similarly, every base produces its conjugate acid as a result of accepting a proton.
For example, acetate ion is the conjugate base of acetic acid, and ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of ammonia.
As the acid of a conjugate acid/base pair becomes weaker, its conjugate base becomes stronger and vice versa.
A further extension of the idea of acids and bases was made in the Lewis theory. In this, a G. N. Lewis acid is a compound or atom that can accept a pair of electrons and a Lewis base is one that can donate an electron pair. This definition encompasses "traditional" acid-base reactions, but it also includes reactions that do not involve ions, e.g.
in which NH3 is the base (donor) and BCl3 the acid (acceptor).
acid radical → kiseli radikal
Acid radical is an anion left after removal of hydrogen atoms from an acid.
acid salt → kisela sol
Acid salt is a compound formed by replacing hydrogen in an acid with a metal (or a radical that acts like a metal).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vodik." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table