body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
body-centered orthorhombic lattice → prostorno centrirana ortorompska rešetka
Body-centered orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
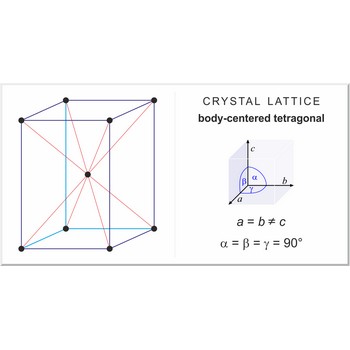
body-centered tetragonal lattice → prostorno centrirana tetragonska rešetka
Body-centered tetragonal lattice (tetragonal-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
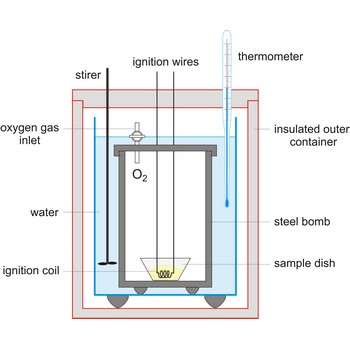
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
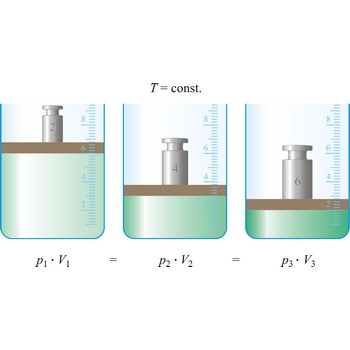
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
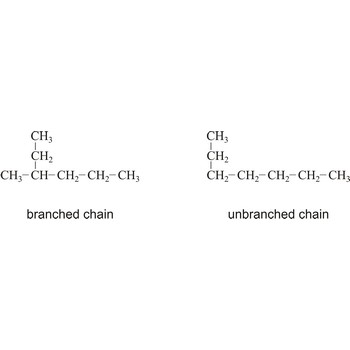
branched chain → razgranati lanac
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
brass → mjed
Brasses are alloys of copper and zinc (generally 5 % to 40 %). Brass has been known to man since prehistoric times, long before zinc itself was discovered. It was produced by melting copper together with calamine, a zinc ore. Its ductility reaches a maximum with about 30 % zinc and its tensile strength with 45 % although this property varies greatly with the mechanical and heat treatment of the alloy. Typical applications included gears, plumbing ware fittings, adapters, valves and screw machine products. The French horn is a valved brass wind instrument.
Brass may contain small amounts of other alloying elements, such as aluminum, lead, tin, or nickel. Lead can be added as an alloying element resulting in a brass that can be rapidly machined and produces minimal tool wear. Additions of aluminium, iron and manganese to brass improve strength, whilst silicon additions improve wear resistance. Brass containing tin (< 2 % ) is less liable to corrosion in seawater; it is sometimes called naval brass and is used in naval construction.

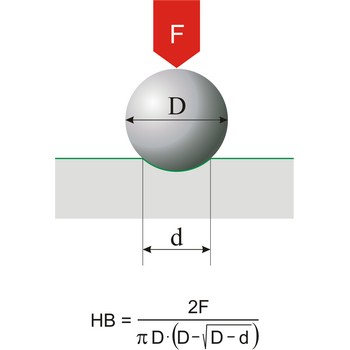
Brinell hardness → Brinellova tvrdoća
Brinell hardness is a scale for measuring the hardness of metals introduced around 1900 by Swedish metallurgist Johan Brinell (1849-1925). A small chromium steel ball is pressed into the surface of the metal by a load of known weight. The loading force is in the range of 300 N to 30 000 N. The ratio of the mass of the load in kilograms to the area of the depression formed in square millimetres is the Brinell Hardness Number.
Buchner flask → Buchnerova tikvica
Büchner flask (also known as a vacuum flask, filter flask, side-arm flask or Kitasato flask) is a thick-walled Erlenmeyer flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Visoka peÃâ¡." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table