valence bond → valentna veza
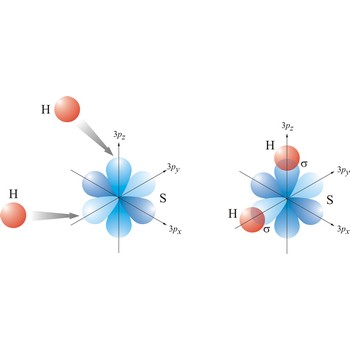
In the valence bond theory, a valence bond is a chemical bond formed by overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals on two different atoms.
metallic bond → metalna veza
Metallic bond is a electrostatic attraction binding the positive ions of a solid metal together by means of a "sea" of delocalised valence electrons
sigma bond → sigma veza
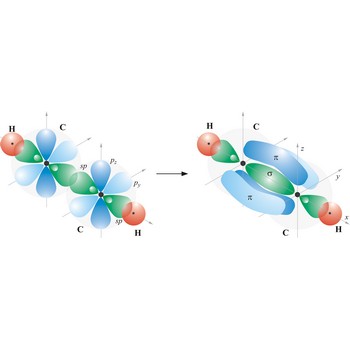
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
triple bond → trostruka veza
Triple bond. (≡) is a covalent bond that involves 3 bonding pairs. In the valence bond theory, one of the bonds in a triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds. For example, the central bond in acetylene is a triple bond: H-C≡C-H.
valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
conjugated bond → konjugirana veza
Conjugated bonds describe the alternating pattern of double and single bonds, or triple bonds and single bonds, in a molecule. In such molecules, there is some delocalisation of electrons into the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms linked by the single bond.
conjugated double bond → konjugirana dvostruka veza
Conjugated double bond in organic compounds is a system of double bonds between atoms which are separated by one single bond (1,3-butene, H2C=CH-CH=CH2).
cumulated double bond → kumulirana dvostruka veza
Cumulated double bond in organic compounds is a system of two double bonds on the same atom of carbon (C=C=C)
covalent bond → kovalentna veza
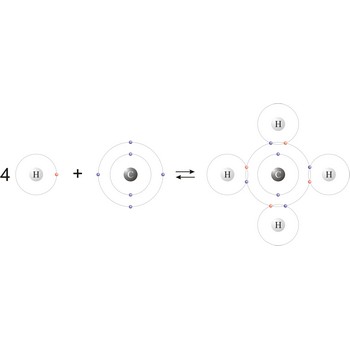
Covalent bond is a chemical bond between two atoms whose stability results from the sharing of two electrons, one from each atom (H· + ·H = H:H or H-H).
polar covalent bond → polarna kovalentna veza
Polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the electrons are not equally shared because one atom attracts them more strongly than the other
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Valentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table