practical salinity → praktični salinitet
Practical salinity SP is defined on the Practical Salinity Scale of 1978 (PSS-78) in terms of the conductivity ratio K15 which is the electrical conductivity of the sample at temperature t68 = 15 °C and pressure equal to one standard atmosphere, divided by the conductivity of a standard potassium chloride (KCl) solution at the same temperature and pressure. The mass fraction of KCl in the standard solution is 0.0324356 (32.4356 g of KCl in 1 kg of solution). When K15 = 1, the Practical Salinity P S is by definition 35. The conductivity of that reference solution is C(35,1568,0) = 42.914 mS/cm = 4.2914 S/m (Siemens per meter). Note that Practical Salinity is a unit-less quantity. Though sometimes convenient, it is technically incorrect to quote Practical Salinity in "psu". When K15 is not unity, SP and K15 are related by the PSS-78 equation
At a temperature of t68 = 15 °C, Rt is simply K15 and Practical Salinity SP can be determined from the above equation. For temperatures other than t68 = 15 °C, Practical Salinity SP is given by the following function of Rt (k = 0.0162)
silicon → silicij
Silicon was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1824. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word silicis meaning flint. Amorphous form of silicon is brown powder; crystalline form has grey metallic appearance. Solid form unreactive with oxygen, water and most acids. Dissolves in hot alkali. Silica dust is a moderately toxic acute irritant. Silicon makes up major portion of clay, granite, quartz and sand. Commercial production depends on a reaction between sand (SiO2) and carbon at a temperature of around 2200 °C. Used in glass as silicon dioxide (SiO2). Silicon carbide (SiC) is one of the hardest substances known and used in polishing. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors.
silver coulometer → srebrni kulometar
Silver coulometer consists of a platinum vessel which acts as a cathode and contains a solution of pure silver nitrate as an electrolyte (c(AgNO3) = 1 mol/L). A rod of pure silver enclosed in a porous pot acts as the anode. The current density at the anode should not exceed 0.2 Acm-2. After electrolysis, the electrolyte is taken out and the platinum vessel is washed, dried and weighed. The increase in the weight gives the amount of silver deposited (96500 C of electricity deposits 107.88 g of silver). From the mass of the silver deposited, the coulomb involved in the reaction can be calculated.
starch → škrob
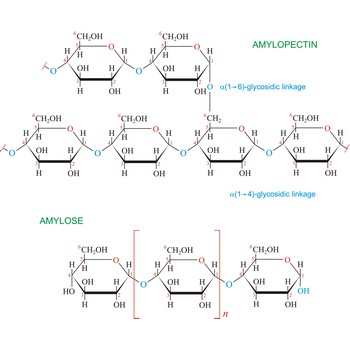
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
supercritical fluid chromatography → superkritična fluidna kromatografija
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a hybrid of gas and liquid chromatography. SFC is of importance because it permits the separation and determination of a group of compounds that are not conveniently handled by either gas or liquid chromatography. These compounds are either nonvolatile or thermally labile so that gas chromatography cannot be used and they do not contain functional groups that make possible detection by liquid chromatography. SFC has been applied to a wide variety of materials including natural prodcuts, drugs, foods, pesticides and herbicides, fossil fuels, explosives and propellants.
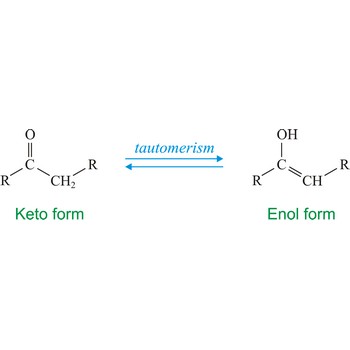
tautomerism → tautomerija
Tautomerism refers to equilibrium between two different structures of the same compound. Usually the tautomers differ in the point of attachment of a hydrogen atom. One of the most common examples of a tautomeric system is the equilibrium between a ketone (keto) and aldehyde (enol).
thermometer → termometar
Thermometers are devices for measuring temperature. Linear and volume thermal expansion are macroscopic properties of matter, which can be easily measured, relative to measurements of microscopic properties, on the basis of which, temperature is defined. Thermometers based on thermal expansion are secondary instruments that is, they have to be calibrated in comparison to a standard thermometer. In a thermometer with liquid, mercury or alcohol is placed in a small glass container. If temperature increases, the liquid undergoes volume expansion and rises in a capillary. The level of the raised liquid is the measure of temperature. Mercury thermometers measure temperatures in the temperature range between -39 °C and 300 °C. Alcohol thermometers measure lower temperatures. Bimetal thermometers have a spiral spring, which consists of two metals with different coefficients of linear expansion. When temperature changes, metals undergo different change in length and the consequence twisting of the spring is transferred to a pointer, the deflection of which is the measure of temperature.
zinc → cink
Zinc was discovered by Andreas Marggraf (Germany) in 1746. The origin of the name comes from the German word zink. It is bluish-silver, ductile metal. Reacts with alkalis and acids. Tarnishes in air. Zinc is found in the minerals zinc blende (sphalerite) (ZnS), calamine, franklinite, smithsonite (ZnCO3), willemite and zincite (ZnO). Used to coat other metal (galvanizing) to protect them from rusting. Although some 90 % of the zinc is used for galvanizing steel. Zinc metal is used in the common dry-cell battery. Also used in alloys such as brass, bronze. Zinc compounds are also used in the manufacture of paints, cosmetics, plastics, electronic devices, and other products.
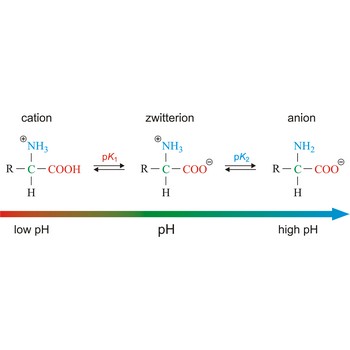
zwitterion → dipolarni ion
Zwitterion, also known as inner salt or dipolar ion, is an ion with a positive and a negative electrical charge at different locations within a molecule. As the molecule contains two opposite charges, it is electrically neutral. The term zwitterion is derived from the German word zwitter, meaning a hybrid, hermaphrodite. Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and base groups in their molecules (ampholytes).
All of the common amino acids found in proteins are ampholytes because they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) that acts as an acid and an amino group (-NH2) that acts as a base. In the solid state, amino acids exist in the dipolar or zwitterion form. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
Schrotter apparatus for determination of CO2 → Schrotterova aparatura za određivanje CO2
Schrötter decomposition apparatus (Schrötter's alkalimeter) is used to determining the carbonate content in samples of limestone, gypsum, dolomite, or baking powder by loss of weight. The apparatus is named after the Austrian chemist Anton Schrötter von Kristelli (1802-1875), who devised it in 1871. The size of the filled apparatus (apparatus is 16 cm high) is such that it weights less than 75 g, and can be placed on the pan of an analytical balance.
Procedure: Weigh about 0.5 g of the powdered carbonate sample and introduce it into the decomposition flask C. Pour into the drying tube A 2-3 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and to the dropping funnel B add about 10-15 mL of hydrochloric acid (w(HCl) = 15 %). Weigh the whole apparatus. Open the upper taps of both parts and allow the hydrochloric acid from B to run slowly down on to the powdered sample. The evolved CO2 escapes through the strong sulphuric acid and is thus thoroughly dried. When further addition of acid produces no more evolution of CO2, warm the apparatus up to 80 °C so as to expel the CO2 from the solution. Connect the upper tap of the drying tube A to a water pump and draw a slow current of air through the apparatus until completely cool. Open the upper taps for a moment to equalize the internal and external pressure and weight the apparatus again. The weight loss is equal to the weight of carbon dioxide liberated from the carbonates.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vaga s različitim krakovima." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table