chiral centre → kiralno središte
Chiral centre in organic chemistry is most often an asymmetrically substituted carbon atom (C*).
chiral molecule → kiralne molekule
Chiral molecule is a molecule which cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. A common example is an organic molecule containing a carbon atom to which four different atoms or groups are attached. Such molecules exhibit optical activity, i.e., they rotate the plane of a polarised light beam.
chromium → krom
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (France) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. Produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Used to make stainless steel. It gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology.
dehydrogenation → dehidrogenacija
Dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen is removed from a compound. Dehydrogenation of organic compounds converts single carbon-carbon bonds into double bonds. It is usually affected by means of a metal catalyst or in biological systems by enzyme dehydrogenases.
diazo compounds → diazo-spojevi
Diazo compounds are compounds having the divalent diazo group, =N+=N-, attached to a carbon atom. The term includes azo compounds, diazonium compounds, and also such compounds as diazomethane, CH2=N2.
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
conformation → konformacija
Conformation is one of the very large numbers of possible spatial arrangements of atoms that can be interconverted by rotation about a single bond in a molecule. The conformation of a molecule is not fixed, though one or another shape may be more likely to occur. There are two extreme cases:
Staggered conformation (antiperiplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as far apart as possible from the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
Eclipsed conformation (syn-periplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as close as possible to the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
cracking → krekiranje
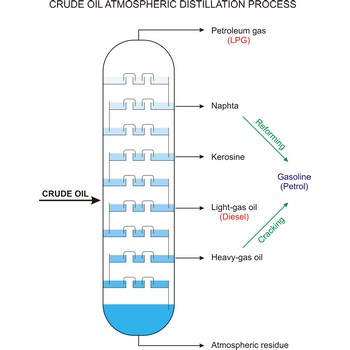
Cracking is the process whereby heavy molecules of petroleum or crude oil are broken down into hydrocarbons of lower molecular weight (especially in the oil-refining process).
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ugljik." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table