global warming → globalno zatopljenje
Global warming or greenhouse effect is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of certain gases (greenhouse gases) that absorb infrared radiation. Light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun is able to penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. This energy is re-radiated as infrared radiation which because of its longer wavelength, is absorbed by such substances as carbon dioxide. The overall effect is that the average temperature of the Earth and its atmosphere is increasing (so-called global Warming). The effect is similar to that occurring in a greenhouse, where light and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation can pass through the glass into greenhouse but the infrared radiation is absorbed by the glass and part of it is re-radiated into the greenhouse.
The greenhouse effect is seen as a major environmental hazard. Average increases in temperature could change weather patterns and agricultural output. It might also lead to melting of the polar ice caps and a corresponding rise in sea level. Carbon dioxide, from fossil-fuel power stations and car exhausts, is the main greenhouse gas. Other contributory pollutants are nitrogen oxides, ozone, methane, and chloroflourocarbons.
halocarbon → halogenirani ugljikovodik
Halocarbon is a compound containing no elements other than carbon, one or more halogens, and sometimes hydrogen. The simplest are compounds such as tetrachloromethane (CCl4), tetrabromomethane (CBr4), etc. The lower members of the various homologous series are used as refrigerants, propellant gases, fireextinguishing agents, and blowing agents for urethane foams. When polymerized, they yield plastics characterized by extreme chemical resistance, high electrical resistivity, and good heat resistance.
thermit welding → termitno zavarivanje
Thermit welding is a group of welding processes in which fusion is produced by heating with superheated liquid metal resulting from a chemical reaction between a metal oxide and aluminium.
thermodynamics → termodinamika
Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other forms of energy.
zero law of thermodynamics → nulti zakon termodinamike
Zero law of thermodynamics states: If some body A is in thermal equilibrium with body B and with body C, then bodies B and C are also in thermal equilibrium.
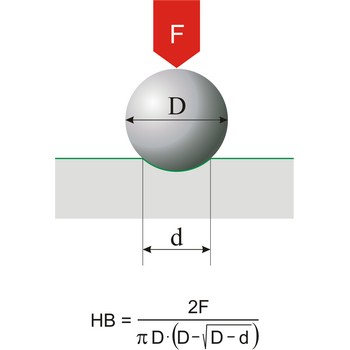
hardness → tvrdoća
Hardness is the resistance of a material to deformation of an indenter of specific size and shape under a known load. This definition applies to all types of hardness scales except Mohs scale, which is a based on the concept of scratch hardness and is used chiefly for minerals. The most generally used hardness scales are Brinell (for cast iron), Rockwell (for sheet metal and heat-treated steel), Knoop (for metals).
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
Nusselt number → Nusseltova značajka
Nusselt number (Nu) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechan-ics, defined by
where h is coefficient of heat transfer, l is length, and k is thermal conductivity.
Peclet number → Pecletova značajka
Péclet number (Pe) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where v is velocity, l is length, and a is thermal diffussivity.
plastic → plastika
Plastic is a material that can be shaped by the application of heat or pressure. Most are based on synthetic polymers although some are the product of natural substances (such as cellulose derivatives, but excluding the rubbers.). They are usually light and permanent solids, being also heat and electric isolators. If the materials soften again when reheated, they are said to be thermoplastic. If, after fashioning, they resist further applications of heat, they are said to be thermoset.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Toplinsko rastezanje." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table