Nusselt number → Nusseltova značajka
Nusselt number (Nu) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechan-ics, defined by
where h is coefficient of heat transfer, l is length, and k is thermal conductivity.
superfluid helium → superfluidni helij
Superfluidity in helium-4 was discovered in 1938 by the Soviet physicist Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa. Helium-4 exhibits superfluidity when it is cooled below 2.18 K (-270.97 C), which is called the lambda (λ) point. At these temperatures, helium-4 exhibits the characteristics of two distinct fluids, one of which appears to flow without friction. An extensive series of experiments showed that in this state of helium, called helium II (He II), there is an apparent enormous rise in heat conductivity, at an increase rate of about three million. Another unusual property of He II is its mobile, rapid flow through capillaries or over the rim of its containment vessel as a thin film that exhibits no measurable viscosity and appears unaffected by the forces of gravity or evaporation and condensation.
absolute zero → apsolutna nula temperature
Absolute zero is theoretically, the lowest attainable temperature. It is the energy at which the kinetic energy of atom and molecules is minimal and is equivalent to -273.15 °C.
blackbody → crno tijelo
In radiation physics, an ideal blackbody is a theoretical object that absorbs all the radiant energy falling upon it and emits it in the form of thermal radiation. Planck’s radiation law gives the power radiated by a unit area of blackbody, and the Stefan-Boltzman law expresses the total power radiated.
blanching → blanširanje
1. Blanching is a heat treatment of foodstuffs to partially or completely inactivate the naturally occurring enzymes prior to freezing.
2. Blanching is a washing process for coins cleaning. The black surface layer of cupric oxide is removing by dipping the coins in hot dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %).
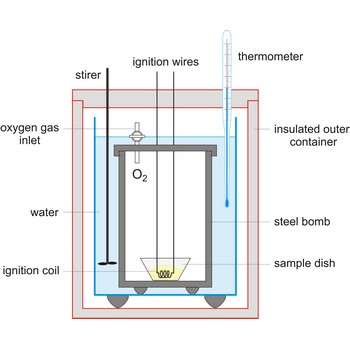
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
conduction → kondukcija
This process occurs most significantly in solids. The atoms or molecules in a solid state do not leave their mean positions, but continue to vibrate about their mean positions. They transfer heat energy from one atom to another. This happens because of the coupling between them due to mutually attractive forces.
conductometry → konduktometrija
Conductometry is a volumetric analytic method in which the end of titration (equivalent point) is defined by an electric conductivity appliance.
Glauber’s salt → Glauberova sol
Glauber’s salt is sodium sulphate decahydrate (Na2SO4·10H2O). Loses water of hydration at 100 °C. Energy storage capacity is more than seven times that of water.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Toplinska vodljivost." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table