polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
refractometer → refraktometar
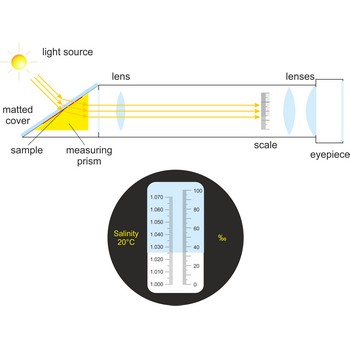
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
resistance → električni otpor
Electrical resistance (R) of a given object is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that object. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω). Resistance is the electric potential difference divided by the current when there is no electromotive force in the conductor. This definition applies to direct current. For a conductor of uniform cross section with area A and length L, and whose resistivity is ρ, the resistance is given by
significant figures → značajne znamenke
Measurements are not infinitely accurate: we must estimate measurement uncertainty. The number of significant figures is all of the certain digits plus the first uncertain digit.
Rules for significant figures:
- Disregard all initial zeros.
- Disregard all final zeros unless they follow a decimal point.
- All remaining digits including zeros between nonzero digits are significant.
| 0.0023 | has two significant figures |
| 0.109 | has three significant figures |
| 2.00 | has three significant figures |
| 70 | has one significant figure |
In addition and subtraction, the number of significant figures in the answer depends on the original number in the calculation that has the fewest digits to the right of the decimal point.
In multiplication and division, the number of significant figures in a calculated result is determined by the original measurement that has the fewest number of significant digits.
In a logarithm of a number, keep as many digits to the right of the decimal point as there are significant figures in the original number.
In an antilogarithm of a number, keep as many digits as there are digits to the right of the decimal point in the original number.
simple magnifier → lupa
Simple magnifier is a converging lens, placed between the object and the eye, with the object inside the focal length of the lens. The angular magnification of a simple magnifier is:
where f is the focal length of the lens and 15 cm is the near point distance for a normal eye. The image of the object is virtual, which means that the rays do not actually pass through the point of intersection, that is, it can not be seen on a screen.
thermal resistance → toplinski otpor
Heat always flows from a higher to a lower temperature level. The driving force for the heat flux lies in the temperature difference ΔT between two temperature levels. Analogous to Ohm’s law, the following holds:
where H = dQ/dt is heat flux, measured in watts, ΔT is temperature difference across the thermal resistance, measured in kelvin, and Rth is thermal resistance, measured in K/W.
For example, suppose there were two houses with walls of equal thickness; one is made of glass and the other of asbestos. On a cold day, heat would pass through the glass house much faster. The thermal restistance of asbestos is then higher than of glass.
If the thermal Ohm’s law is divided by the heat capacity C, Newton’s law of cooling is obtained:
where dT/dt is rate of cooling or heating, measured in K s-1, and C is heat capacity, measured in J K-1.
starch → škrob
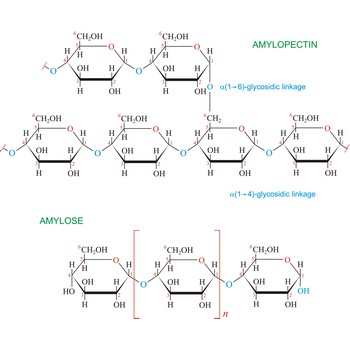
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
thermosetting plastic → termostabilna plastika
Thermosetting plastics (thermosets) refer to a range of polymer materials that cure, through the addition of energy, to a stronger form. The energy may be in the form of heat (rubber), through a chemical reaction (two part epoxy), or irradiation. Thermoset materials are usually liquid or malleable prior to curing, and designed to be molded into their final form, or used as adhesive.
Thermoset polymer resins transformed into plastics or rubbers by cross-linking into a rigid, 3-D structure. A thermoset material cannot be melted and re-molded after it is cured.
wash bottle → boca štrcaljka
Plastic wash bottle is a squeeze bottle made of low density polyethylene (LDPE) whose contents can be forced out through a narrow hole at the top by squeezing the bottle.
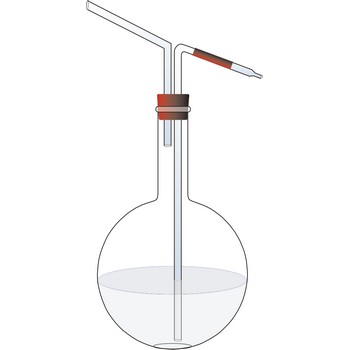
Glass wash bottle is a bottle fitted with two glass tubes pass through the cap, so that on blowing into one of the tubes a stream of water issuing from the other may be directed upon anything to be washed or rinsed, as a precipitate upon a filter.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "To pass final judgement中文." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table