Coulomb’s law → Coulombov zakon
Coulomb’s law is the statement that the force F between two electrical charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance r is
where εo is the permittivity of a vacuum, equal to
absorbance → apsorbancija
Absorbance (A) is a logarithm of the ratio of incident radiant power (Po) to transmitted radiant power (P) through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls).
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
Avogadro, Amadeo → Avogadro, Amadeo
Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856) is an Italian chemist and physicist that proposed a correct molecular explanation for Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes. His work provided a simple way to determine atomic weights and molecular weights of gases. He is published a theory about the movement of particles in gases that became known as Avogadro’s Law.
coulometry → kulometrija
Coulometry is a quantitative electrochemical analytical method which is based on measuring the quantity of electricity that has passed and on Faraday’s laws.
crystallography → kristalografija
Crystallography is a science that studies structure, shapes, crystalline properties and laws of their creation.
Dalton, John → Dalton, John
Dalton, John (1766-1844) British chemist and physicist. In 1801 he formulated his law of partial pressures (Dalton’s law), but he is best remembered for Dalton’s atomic theory, which he announced in 1803. Dalton also studied colour blindness (a condition, once called Daltonism, that he shared with his brother).
environment protection → zaštita okoliša
From Environment protection law of the Republic of Croatia: By protection of the environment, the following is ensured: complete preservation of environment quality, natural community preservation, rational usage of natural resources and energy in the most favourable way concerning the environment as a basic condition of healthy and sustainable development.
equation of state → jednadžba stanja
Equation of state is an equation relating the pressure, volume, and temperature of a substance or system. Equation of state for ideal gas
where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
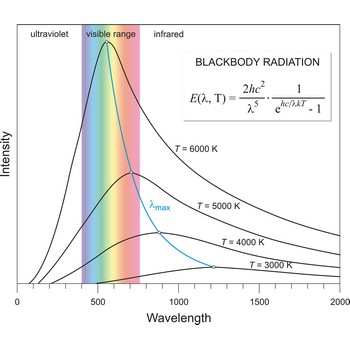
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Termodinamički zakoni." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table