crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
desiccator → eksikator
Desiccator is a glass container with dry atmosphere due to the presence of some dehydrating agent. It is used for protecting the samples, reagents or precipitates from humidity. As dehydrating agent usually waterless calcium chloride (CaCl2) is used.
salt fog chambers → slana komora
Salt fog chambers are designed for corrosive atmosphere testing. The samples being tested are inserted into the chamber and then the salt-containing solution is sprayed as a very fine fog mist over the samples. The temperature within the chamber is maintained constant (usually 35 °C). These test chambers are constructed of non-corrosive materials.
Einstein, Albert → Einstein, Albert
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) is a German born American physicist, who took Swiss nationality in 1901. A year later he went to work in the Bern patent office. In 1905. he published five enormously influential papers, one on Brownian movement, one on the photoelectric effect, one on the special theory of relativity, and one on energy and inertia (which included the famous expression E = mc2). In 1915 he published the general theory of relativity, concerned mainly with gravitation. In 1921 he was awarded the Nobel Prize. In 1933, as a Jew, Einstein decided to remain in the USA (where he was lecturing), as Hitler had come to power. For the remainder of his life he sought a unified field theory. In 1939 he informed president Roosevelt that an atom bomb was feasible and that. Germany might be able to make one.
enthalpy → entalpija
Enthalpy (H) is a thermodynamic property of a system defined by
where U is the internal energy of the system, p its pressure, and V its volume. J.W. Gibbs put the concept of an ensemble forward in 1902. In a chemical reaction carried out in the atmosphere the pressure remains constant and the enthalpy of reaction (ΔH), is equal to
For an exothermic reaction ΔH is taken to be negative.
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
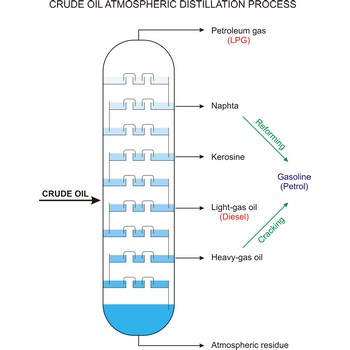
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
freon → freon
Freon (chlorofluorocarbon, CFC) a type of compound in which some or all of the hydrogen atoms of hydrocarbon (usually an alkane) have been replaced by chlorine and fluorine atoms. Most CFC are chemically uncreative and are stable at high temperatures. They are used as aerosol propellants, refrigerants, and solvents, and in the manufacture of rigid packaging foam. CFC because of their chemical inertness, can diffuse unchanged into the upper atmosphere. Here, photochemical reactions cause them to break down and react with ozone. For his reason, their use has been discouraged.
global warming → globalno zatopljenje
Global warming or greenhouse effect is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of certain gases (greenhouse gases) that absorb infrared radiation. Light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun is able to penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. This energy is re-radiated as infrared radiation which because of its longer wavelength, is absorbed by such substances as carbon dioxide. The overall effect is that the average temperature of the Earth and its atmosphere is increasing (so-called global Warming). The effect is similar to that occurring in a greenhouse, where light and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation can pass through the glass into greenhouse but the infrared radiation is absorbed by the glass and part of it is re-radiated into the greenhouse.
The greenhouse effect is seen as a major environmental hazard. Average increases in temperature could change weather patterns and agricultural output. It might also lead to melting of the polar ice caps and a corresponding rise in sea level. Carbon dioxide, from fossil-fuel power stations and car exhausts, is the main greenhouse gas. Other contributory pollutants are nitrogen oxides, ozone, methane, and chloroflourocarbons.
Haber process → Haberov proces
Haber process is an industrial process for producing ammonia by reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen:
The reaction is reversible and exothermic, so that a high yield of ammonia is favoured by low temperature. However, the rate of reaction would be too slow for equilibrium to be reached at normal temperatures, so an optimum temperature of about 450 °C is used, with a catalyst of iron containing potassium aluminium oxide promoters. The higher the pressure the greater the yield, although there are technical difficulties in using very high pressures. A pressure of about 250 atmospheres is commonly employed. The removal of ammonia from the batch as soon as it is formed ensures that an equilibrium favouring product formation is maintained. The nitrogen is obtained from air. Formerly, the hydrogen was from water gas and the water-gas shift reaction (the Bosch process) but now the raw material (called synthesis gas) is obtained by steam reforming natural gas.
The process is of immense importance for the fixation of nitrogen for fertilisers and explosives. It was developed in 1908 by German chemist Fritz Haber (1868-1934) and was developed for industrial use by Carl Bosch (1874-1940), hence the alternative name Haber-Bosch process.
hydrogen → vodik
Hydrogen was discovered by Sir Henry Cavendish (England) in 1766. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words hydro and genes meaning water and generate. It is colourless, odourless gas, burns and forms explosive mixtures in air. Reacts violently with oxidants. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. Commercial quantities of hydrogen are produced by reacting superheated steam with methane or carbon. In lab work from reaction of metals with acid solutions or electrolysis. Most hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia and in metal refining. Also used as fuel in rockets. Its two heavier isotopes (deuterium and tritium) used respectively for nuclear fusion.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Tehnička atmosfera." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table