chalcogens → halkogeni elementi
Chalcogens are the Group 16 elements: oxygen (O), sulphur (S), selenium Se), tellurium (Te), and polonium (Po). Compounds of these elements are called chalcogenides.
chemical compound formula → formula kemijskog spoja
Chemical elements are represented by their symbols, and chemical compounds are represented by a group of symbols of those elements from which the compound is composed. That group of symbols, which shows which atoms and in which number relation they are present in certain compound is called a chemical compound formula.
In a formula chemical symbols show which element is present in a certain compound, and its index shows how much of that element there is in a certain compound. From sulphuric acid formula H2SO4 we can see that one molecule of sulphuric acid consists of two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of sulphur and four atoms of oxygen.
coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
composition of ocean water → sastav oceanske vode
The proportions of the major constituents of ocean water are almost constant throughout the world. Salinity (total salt content) and the concentrations of individual chemical constituents in sea wateris given the units psu (practical salinity units). For most purposes one can assume that the new unit, psu, and the older unit, ‰, are synonymous.
The average composition of the ocean water is as shown on the following table.
| Constituent | Percentage of total salt |
|---|---|
| Chlorine | 55.3 % |
| Sodium | 30.8 % |
| Magnesium | 3.7 % |
| Sulphur | 2.6 % |
| Calcium | 1.2 % |
| Potassium | 1.1 % |
heterocyclic compounds → heterociklički spojevi
Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds having as ring members atoms of at least two different elements, e.g., quinoline, 1,2-thiazole.
contact procedure → kontaktni postupak
Contact procedure is an industrial procedure used for the production of sulphuric acid, where a dry and clean sulphur dioxide and air go over a catalyst made of vanadium pentoxide at 450 °C by which sulphur trioxide is gained, then we add concentrated sulphuric acid by which we obtain smoking sulphuric acid which is now diluted to sulphuric acid.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
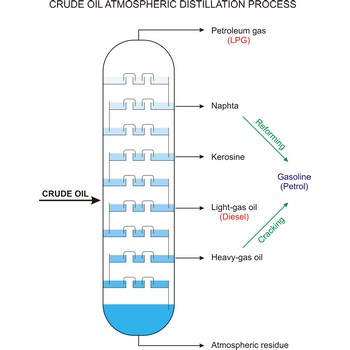
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sumpor." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table