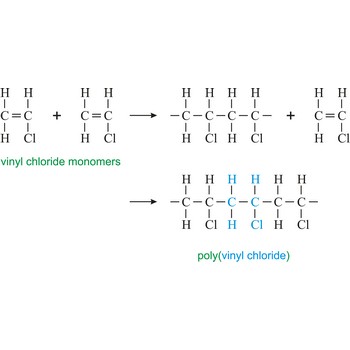
degree of polymerisation → stupanj polimerizacije
Degree of polymerisation is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or an oligomer molecule.
Celsius → Celzijev stupanj
Celsius (°C) is a common but non-SI unit of temperature, defined by assigning temperatures of 0 °C and 100 °C to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
degree → stupanj
1. Degree is a unit of temperature on a specified scale. The temperatures of boiling and freezing water are: in the Fahrenheit system 212 and 32 degrees; in the Celsius system 100 and 0 (zero) degrees.
2. Degree is a unit of angular measure. A circle is divided into 360 degrees, represented by the symbol °. Degrees are each divided into 60 minutes. Each minute has 60 seconds. Symbols for degree, minute, and second for plane angle is placed after the numerical value and a no space between the numerical value and the unit symbol (α = 2°3'4").
3. In algebra, the degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. For example, 4x3 + 3x2 + x + 7 have degree 3.
condensational polymerisation → kondenzacijska polimerizacija
Condensational polymerisation is a reaction of polymerisation in which monomers together create a polymer by losing small molecules like water.
polymerization → polimerizacija
Polymerization is a reaction of connecting many monomers in one long molecule whereby polymers are created.
acrylic acid → akrilna kiselina
Acrylic acid (propenoic acid) is a colourless liquid, smelling like acetic acid. It can be formed by acrolein oxidation. It readily polymerizes and is used in the manufacture of acrylic resins, transparent plastic materials (organic glass).
Celsius temperature scale → Celsiusova temperaturna skala
For value of zero in Celsius temperature scale the freezing point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken as another reference point. This range is divided into 100 equal parts, and each part is an equivalent to 1 °C. Units of Celsius temperature scale (°C) and thermodynamic temperature scale (K) are identical
1 °C = 1 K.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
copolymer → kopolimer
Copolymers are also known as heteropolymers. They are made from two (or more) different monomers, which usually undergo a condensation reaction with the elimination of a simple molecule, such as ammonia or water. A typical example is the condensation of 1,6-diaminohexane (hexamethylenediamine) with hexanedioic acid (adipic acid) to form nylon 6,6.
The properties of a polymeric plastic can most easily be modified if it is a copolymer of two or more different monomers, e.g. acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS). Varying the proportions of the component monomers can preselect its properties.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Stupanj polimerizacije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table