free radical → slobodni radikal
Free radical is a molecular fragment having one or more unpaired electrons, usually short-lived and highly reactive. They can be produced by photolysis or pyrolysis in which a bond is broken without forming ions. In formulas, a free radical is conventionally indicated by a dot (·CH3, ·SnH3, ·Cl). Free radicals are known to be formed by ionising radiation and thus play a part in deleterious degradation effects that occur in irradiated tissue. They also act as initiators or intermediates in oxidation, combustion, photolysis, and polymerisation.
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
half-cell → polučlanak
Half-cell is a part of galvanic cell in which oxidations or reduction of an element in contact with water or water solution one of its compounds.
heat capacity → toplinski kapacitet
Heat capacity is defined in general as dQ/dT, where dQ is the amount of heat that must be added to a system to increase its temperature by a small amount dT. The heat capacity at a constant pressure is Cp = (∂H/∂T)p; that at a constant volume is CV = (∂E/∂T)V, where H is enthalpy, E is internal energy, p is pressure, V is volume, and T is temperature. An upper case C normally indicates the molar heat capacity, while a lower case c is used for the specific (per unit mass) heat capacity.
Hesse’s law → Hessov zakon
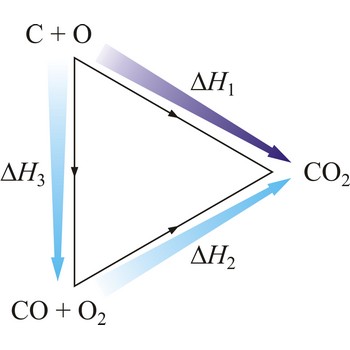
Hesse’s law says that reaction heat of some chemical change does not depend on the way in which the reaction is conducted, but only on starting and ending system state. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. The law was first put forward in 1840 by the Swiss-born Russian chemist Germain Henri Hess (1802-1850).
Hesse’s law can be used to obtain thermodynamic data that cannot be measured directly. For example, it is very difficult to control the oxidation of graphite to give pure CO. However, enthalpy for the oxidation of graphite to CO2 can easily be measured. So can the enthalpy of oxidation of CO to CO2. The application of Hess’s law enables us to estimate the enthalpy of formation of CO.
| C(s) + O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH1 = -393 kJ mol-1 |
| CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH2 = -283 kJ mol-1 |
| C(s) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO(g) | ΔrH3 = -110 kJ mol-1 |
The equation shows the standard enthalpy of formation of CO to be -110 kJ/mol.
indicator → indikator
Indicator is a substance used to show the presence of a chemical substance or ion by its colour. Acid-base indicators are compounds, such as phenolphtaleine and methyl orange, which change colour reversibly, depending on whether the solution is acidic or basic. Oxidation-reduction indicators are substances that show a reversible colour change between oxidised and reduced forms.
molybdenum → molibden
Molybdenum was discovered by Carl William Scheele (Sweden) in 1778. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word molybdos meaning lead. It is silvery white, very hard metal, but is softer and more ductile than tungsten. Molybdenum is found in the minerals molybdenite (MoS2) and wulfenite (MoO4Pb). Its alloys are used in aircraft, missiles and protective coatings in boiler plate.
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Stupanj oksidacije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table