alpaca → alpaka
Alpaca (alpaka) or Nickel Silver is the generic name for any of a range of non-precious bright silvery-grey metal alloys, composed of copper, nickel and zinc. Despite its name it contains no real silver. It is also commonly called German Silver.
There are many different formulations of alloys which fall within the general term of Nickel Silver. All contain copper, nickel and zinc, while some formulations may additionally include antimony, tin, lead or cadmium. A representative formulation is 65 % copper, 18 % nickel, 17 % zinc. Nickel Silver is widely used for the commercial production of industrial components, housewares, flatware and cutlery, and as the metal substrate for silver-plated goods.
aluminium → aluminij
Aluminium was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) in 1827. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word alumen meaning alum. It is soft, lightweight, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces quickly form protective oxide coating. Metal reacts violently with oxidants. Third most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Aluminium is the most abundant metal to be found in the earth’s crust, but is never found free in nature. Aluminium is obtained by electrolysis from bauxite. Used for many purposes from airplanes to beverage cans. Too soft in its pure form so less than 1 % of silicon or iron is added, which hardens and strengthens it.
antioxidant → antioksidans
Antioxidants are compounds that slow down oxidation processes that degrade foods, fuels, rubber, plastic, and other materials. Antioxidants like butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are added to food to prevent fats from becoming rancid and to minimize decomposition of vitamins and essential fatty acids; they work by scavenging destructive free radicals from the food.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
autocatalysis → autokataliza
Autocatalysis is a reaction in which its product can act as a catalyst. Oxalate oxidation with permanganate in an acid solution is a slow reaction
Mn2+-ions catalyse this reaction. When enough Mn2+-ions are created, the reaction occurs instantly.
Celsius temperature scale → Celsiusova temperaturna skala
For value of zero in Celsius temperature scale the freezing point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken as another reference point. This range is divided into 100 equal parts, and each part is an equivalent to 1 °C. Units of Celsius temperature scale (°C) and thermodynamic temperature scale (K) are identical
1 °C = 1 K.
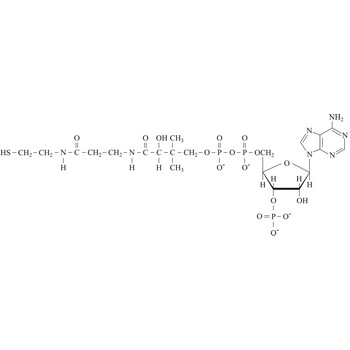
coenzyme a → koenzim a
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
equivalent weight → ekvivalentna masa
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in a neutralization reaction is that mass of substance (molecule, ion, or paired ion) that either reacts with or supplies 1 mol of hydrogen ions in that reaction.
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in an oxidation/reduction reaction is that weight which directly or indirectly produces or consumes 1 mol of electrons.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Stupanj oksidacije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table