catalytic hydrogenation → katalitičko hidrogeniranje
Catalytic hydrogenation is the infusing of unsaturated or impure hydrocarbons with hydrogen gas at controlled temperatures and pressures and in the presence of a catalyst for the purpose of obtaining saturated hydrocarbons and/or removing various impurities such as sulphur and nitrogen.
anhydrous → anhidrid
Anhydrous (without water) is an applied to minerals which do not contain water of crystallization or water of chemical combination. For example, strongly heated copper (II) sulphate pent hydrate (CuSO4•5H2O) produces anhydrous copper (II) sulphate (CuSO4). Less stable and more dangerous to use than hydrated.
aqua regia → zlatotopka
Aqua regia is a mixture of one volume part of nitric acid (HNO3) and three volume parts of hydrochloric acid (HCl). Dissolving of gold in aqua regia is described by the following equation:
arsenic → arsen
Arsenic was discovered by Albertus Magnus (Germany) in 1250. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word arsenikon meaning yellow orpiment. It is steel-grey, brittle semi-metal. Resists water, acids and alkalis. Tarnishes in air, burns in oxygen. Highly toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Arsenic is found in mispickel (arsenopyrite). Many of its compounds are deadly poison and used as weed killer and rat poison. Used in semiconductors. Some compounds, called arsenides, are used in the manufacture of paints, wallpapers and ceramics.
Celsius → Celzijev stupanj
Celsius (°C) is a common but non-SI unit of temperature, defined by assigning temperatures of 0 °C and 100 °C to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
chemical property → kemijsko svojstvo
Chemical property is a property observed when a substance undergoes a transformation into one or more new substances. Measurement of a chemical property involves a chemical change. For example, determining the flammability of petrol involves burning it, producing carbon dioxide and water.
chlorination → kloriranje
1. Chlorination is an addition or substitution of chlorine in organic compounds.
2. Chlorination is a sterilisation of drinking and swimming pool water or oxidation of undesirable impurities, using chlorine or its compounds.
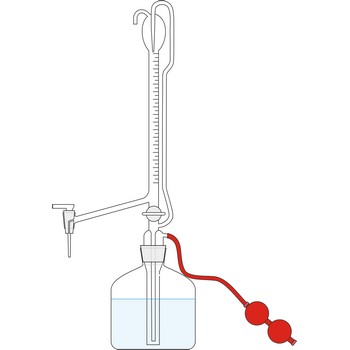
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
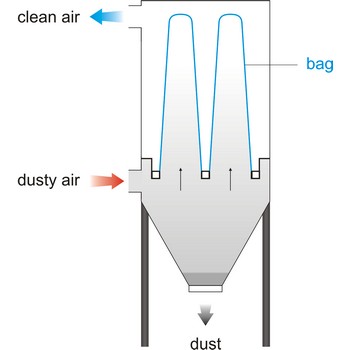
bag filter → vrećasti filtar
Bag filter is a unit within a mechanical system that bellows in a bag form when air flows through, cleaning the air by collecting particles of foreign matter. This system of filtering is rated the most efficient- in a range of 92 % to 95 %. Vacuum cleaner have a cloth filter bag.
Bag filter system is an economical method of liquid filtration consisting of the pressure vessel, restrainer basket and micron rated filter bag. Liquid flow is from the inside to the outside of the bag - dirt is trapped inside the bag.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Standardna prosječna oceanska voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table