salinity → salinitet
Salinity (S) is a measure of the quantity of dissolved salts in seawater. It is formally defined as the total amount of dissolved solids in seawater in parts per thousand (‰) by weight when all the carbonate has been converted to oxide, the bromide and iodide to chloride, and all organic matter is completely oxidized.
Chlorinity is the oldest of the salinity measures considered and is still a corner-stone in the study of dissolved material in seawater. Based on the principle of constant relative proportions it provides a measure of the total amount of dissolved material in seawater in terms of the concentration of halides. The relationship between chlorinity (Cl) and salinity as set forth in Knudsen’s tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Practical Salinity (SP) was introduced as a replacement for Chlorinity. Practical Salinity is is relatively easy to measure using standard conductometers, measurements are more precise and less time consuming than measurements of Chlorinity and accurate measurements can even be made in situ. Practical salinity SP is defined on the Practical Salinity Scale of 1978 (PSS-78) in terms of the conductivity ratio K15 which is the electrical conductivity of the sample at temperature t68 = 15 °C and pressure equal to one standard atmosphere, divided by the conductivity of a standard potassium chloride (KCl) solution at the same temperature and pressure. The mass fraction of KCl in the standard solution is 0.0324356 (32.4356 g of KCl in 1 kg of solution).
Note that Practical Salinity is a unit-less quantity. Though sometimes convenient, it is technically incorrect to quote Practical Salinity in "psu". For most purposes one can assume that the psu and the ‰, are synonymous.
The global average salinity of ocean waters is about 35 ‰, that is, about 35 g of solid substances are dissolved in 1 kg of seawater.
activity → aktivitet
Activity (a) is a thermodynamic function used in place of concentration in equilibrium constants for reactions involving nonideal gases and solutions. For the species i activity is defined as
where ai is the activity of the species i, ci is its molar concentration, and fi is a dimensionless quantity called the activity coefficient.
air stripping → zračni striping
Air stripping is a process for the removal of volatile organic contaminants from groundwater. The groundwater flows downward inside a tower filled with materials (the packing) over a large surface area. Air is introduced at the bottom of the tower and is forced upward past the falling water. The volatiles evaporate from the water and are collected in air filters or released to the atmosphere.
argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
autoxidation → autooksidacija
Autoxidation, autooxidation is a oxidation is caused by exposure to air. Rust is an example of autoxidation. Autoxidation makes ether taken from half-filled bottles very dangerous, because air oxidises ether to highly explosive organic peroxides.
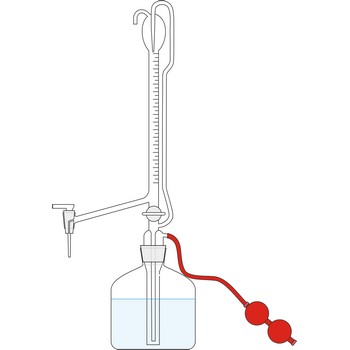
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
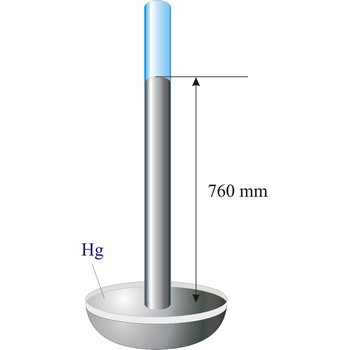
barometer → barometar
Barometer is an instrument that measures atmospheric pressure. A mercury barometer is a closed tube filled with mercury inverted in a mercury reservoir. The height of the mercury column indicates atmospheric pressure (with 1 atm = 760 mm of mercury). An aneroid barometer consists of an evacuated container with a flexible wall. When atmospheric pressure changes, the wall flexes and moves a pointer which indicates the changing pressure on a scale.
Bunsen burner → Bunsenov plamenik
Bunsen burner is a standard source of heat in the laboratory. German chemist Roberts Bunsen (1811-1899) improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. The Bunsen burner has a vertical metal tube through which a fine jet of fuel gas is directed. Air is drawn in through airholes near the base of the tube and the mixture is ignited and burns at the tube’s upper opening. The flow of this air is controlled by an adjustable collar on the side of the metal tube. When the whole is closed a yellow safety flame is displayed. Where as when the whole is open it displays a power dull blue flame with a faint blue outer flame with a vibrant blue core used u for combustion and hearting. The flame can reach temperatures of 1 500 °C.
carbolineum → karbolineum
Carbolineum is a mixture of ingredients of pit coal tar with the boiling point above 270 °C, red-brown oil with tar smell. It is a wood preservative.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Standardna atmosfera." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table