molar enthalpy of evaporation → molarna entalpija isparavanja
Molar enthalpy of evaporation (Δl gH) is a change of enthalpy during evaporation divided by molarity of a liquid, and is equal to the heat energy spent when the evaporation is conducted under constant pressure, Δl gH=Q.
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
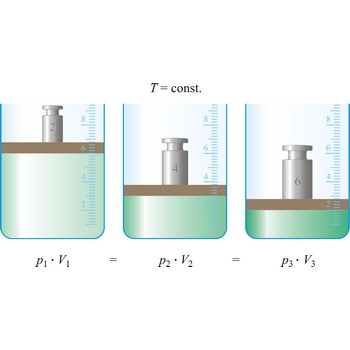
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
Charles’ law → Charlesov zakon
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure expand by the constant fraction of its volume at 0 °C. For each Celsius or kelvin degree its temperature is raised. For any ideal gas fraction it is approximately 1/273. This can be expressed by the equation
were V° is the volume at 0°C and V is its volume at t°C.
This is equivalent to the statement that the volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure is proportional to its thermodynamic temperature
This law also know as Gay-Lussac’s law.
An equation similar to the one given above applies to pressures for ideal gases:
chromium → krom
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (France) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. Produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Used to make stainless steel. It gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology.
molar enthalpy of melting → molarna entalpija taljenja
Molar enthalpy of melting (Δs lH) is a change of enthalpy during melting divided by the molarity of a solid matter, and is equal to the energy used when melting is conducted under constant pressure.
chlorinity → klorinitet
Originally chlorinity (symbol Cl) was defined as the weight of chlorine in grams per kilogram of seawater after the bromides and iodides had been replaced by chlorides. To make the definition independent of atomic weights, chlorinity is now defined as 0.3285233 times the weight of silver equivalent to all the halides.
The Mohr-Knudsen titration method served oceanographers for more than 60 years to determine salinity from chlorinity. This modification of the Mohr method uses special volumetric glassware calibrated directly in chlorinity units. The Mohr method uses potassium chromate (K2CrO4) as an indicator in the titration of chloride ions chloride (plus a small amount of bromide and iodide) with a silver nitrate (AgNO3) standard solution.
The other halides present are similarly precipitated.
A problem in the Mohr titration was that silver nitrate is not well suited for a primary standard. The Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949) suggested that a standard seawater (Eau de mer Normale or Copenhagen Normal Water) be created and distributed to oceanographic laboratories throughout the world. This water was then used to standardize the silver nitrate solutions. In this way all chlorinity determinations were referred to one and the same standard which gave great internal consistency.
The relationship between chlorinity Cl and salinity S as set forth in Knudsen's tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Daniell cell → Daniellov članak
In 1836 the British chemist John Frederic Daniell (1790-1845) proposed an improved electric cell that supplied an even current during continuous operation. Daniell cell consisted of a glass jar containing copper and zinc electrodes, each immersed in their respective acidic sulphate solutions. The two solutions were separated by a porous clay cylinder separator. It was a galvanic cell in which the spontaneous electrodissolution of zinc and electroplating of copper provided the electrical current.
Zn(s) |
→ | Zn2+ + 2e- |
+0.763 V |
Cu2+ + 2e- |
→ | Cu(s) |
+0.337 V |
Zn(s) + Cu2+ |
→← | Zn2+ + Cu(s) |
+1.100 V |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Stalna tvrdoća." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table