lactose → laktoza
Lactose (milk sugar) is a disaccharide comprising one glucose molecule linked to a galactose molecule by an β(1→4)-glycosidic linkage. Lactose has a beta acetal. Lactose is manufactured by the mammary gland and occurs only in milk (from 4 % to 7 %). Lactose intolerance is a common medical condition that results in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and flatulence and is caused by reduced or absent activity of enzyme lactase.
Like cellobiose and maltose, lactose is a reducing sugar. All reducing sugar undergo mutarotation in aqueous solution. The equilibrium mixture at 20 °C is composed of 62.7 % β-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranose) and 37.3 % α-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-glucopyranose).
pigment → pigment
Pigments are the substances that give paint colour. Pigments are derived from natural or synthetic materials that have been ground into fine powders. A pigment is different from a dye in that a pigment is insoluble in the media in which it is used.
Pigment is an organic substance found in plant and animal cells that creates colouring.
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
linear molecular geometry → linearna geometrija molekule
Linear molecule is a molecule in which atoms are deployed in a straight line (under 180° angle). Molecules with an linear electron pair geometries have sp hybridization at the central atom. An example of linear electron pair and molecular geometry are carbon dioxide (O=C=O) and beryllium hydride BeH2.
molecular shape → oblik molekule
Molecular shape is the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in space around a central atom. The molecular formula of a substance does not give an indication of its shape. For example, CO2 is a linear molecule, but SO2 is angular.
The three-dimensional shapes of many small molecules can be predicted by applying the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR). When atoms combine to form molecules, pairs of valence electrons arrange themselves as far from each other as possible. Another way to characterize molecular shape is in terms of hybrid orbitals.
stabiliser → stabilizator
Stabiliser is a substance that makes a mixture more stable. Antioxidants and antiozonants are examples of stabilisers; stabilisers are added to paints to prevent the components of the mixture from separating over time.
nuclear magnetic resonance → nuklearna magnetska rezonancija
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a type of radio-frequency spectroscopy based on the magnetic field generated by the spinning of electrically charged atomic nuclei. This nuclear magnetic field is caused to interact with a very large (1 T - 5 T) magnetic field of the instrument magnet. NMR techniques have been applied to studies of electron densities and chemical bonding and have become a fundamental research tool for structure determinations in organic chemistry.
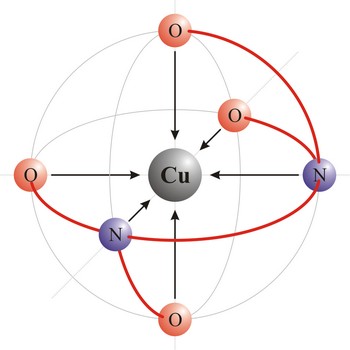
octahedral molecular geometry → oktaedarska geometrija molekule
Octahedral molecular geometry (square bipyramidal shape) describes the shape of compounds where six atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom. The sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), with six bonding pairs, is predicted and found to be a regular octahedron. Four of the attachments are positioned in a square plane with 90° bond angles. The remaining two attachments are positioned perpendicular (90°) to the square plane at opposite ends of the central atom. Molecules with an octahedral electron pair geometries have sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybridization at the central atom.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Spin pair." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table