inertial reference frames → inercijski referentni sustavi
When two frames of reference are moving relative to each other at constant velocity, they are said to be inertial reference frames. The observers from two such inertial frames measure, in general, different velocities of a moving particle. On the other hand, they measure the same acceleration for the particle. The laws of physics must have the same form in all inertial reference frames (the principle of invariance).
international system of units → međunarodni sustav jedinica
International System of Units (SI) is the unit system adopted by the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and recommended for use in all scientific and technical fields. It consists of seven base units (meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, mole, candela), plus derived units and prefixes.
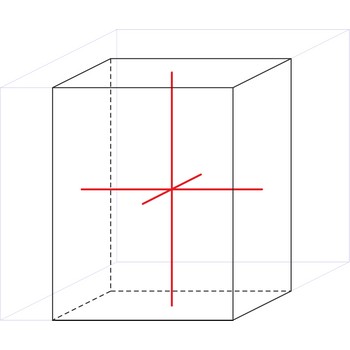
monoclinic crystal system → monoklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the monoclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes. Two of these axes (a and c) are inclined toward each other at an oblique angle; these are usually depicted vertically. The third axis (b) is perpendicular to the other two and is called the ortho axis. The two vertical axes therefore do not intersect one another at right angles, although both are perpendicular to the horizontal axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = γ = 90° ≠ β
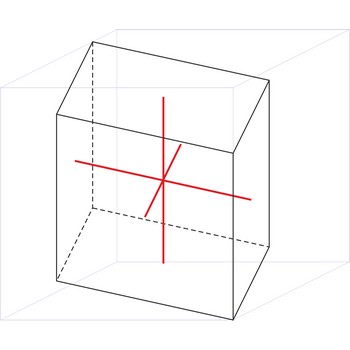
orthorhombic crystal system → ortorompski kristalni sustav
Orthorhombic crystal system is also known as the rhombic system. Minerals of the orthorhombic crystal system are referred to three mutually perpendicular axes, each of which is of a different length than the others.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90°
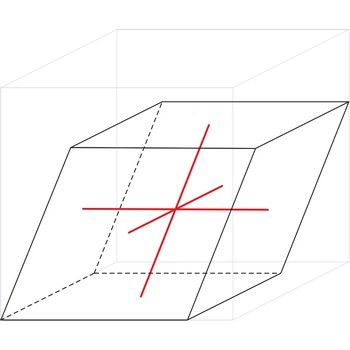
rhombohedral crystal system → romboedarski kristalni sustav
Rhombohedral crystal system is also known as the trigonal system. The crystallographic axes used in this system are of equal length. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a = b = c
α= β = γ ≠ 90°
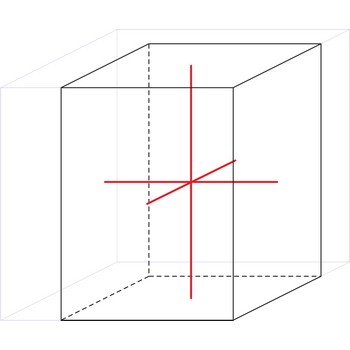
tetragonal crystal system → tetragonski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the tetragonal crystal system are referred to three mutually perpendicular axes. The two horizontal axes are of equal length, while the vertical axis is of different length and may be either shorter or longer than the other two.
a = b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90°
triclinic crystal system → triklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the triclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes, all of which intersect at oblique angles. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
electron configuration → elektronska konfiguracija
The electron configuration shows how many electrons there are in an atom or ion and their distribution along orbitals (see Table of electronic configuration of elements). Structure and all regularity in the periodic system depend upon electronic configuration of atoms of elements. Characteristics of elements mainly depend on electronic configuration of the outer shell. Refilling of the new electronic shell atoms of elements of similar electronic configuration emerge as well as in the previous shell, which adds up to periodicities of characteristics of elements.
lanthanides contraction → kontrakcija lantanoida
Lanthanides contraction is a reduction of metal and ion diameters from lanthanum to lutetium and it is caused by a core charge growth inside the same shell. Elements which in the periodic system of elements come after lanthanides have, because of lanthanides contraction, smaller diameter than they should have according to their position in the periodic system of elements.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Skupine periodnog sustava." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table