polystyrene → polistiren
Polystyrene is a vinyl polymer. Structurally, it is a long hydrocarbon chain, with a phenyl group attached to every other carbon atom. Polystyrene is produced by free radical vinyl polymerization, from the monomer styrene. Polystyrene or Styrofoam is used in the construction industry as insulating material and for production of containers.
substrate → supstrat
1. Substrate is a surface upon which an organism grows, sometimes by using chemicals of particles in the material as food
2. Substrate is a substance that is acted upon by an enzyme during a biochemical reaction.
3. Substrate is the material or product that is to be coated (for example, paint or laminate.).
thermoplastic → termoplastika
Thermoplastic is ap lastic polymer material that can be repeatedly softened through heating and hardened again by cooling. Examples are PVCor polistiren, which when heated, softens to enable moulding and welding, but on cooling hardens. If the finished product is not correct, the material can be heated and manipulated again.
position vector → položajni vektor
The location of a point-like object relative to the origin of a coordinate system is given by a position vector r, which in unit vector notation is
where x, y and z are the scalar components of r.
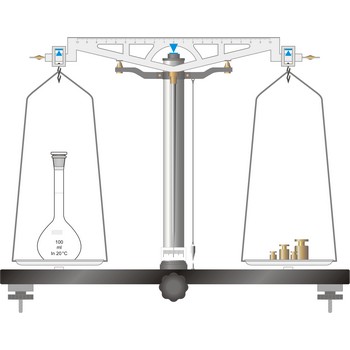
precision balance → tehnička vaga
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
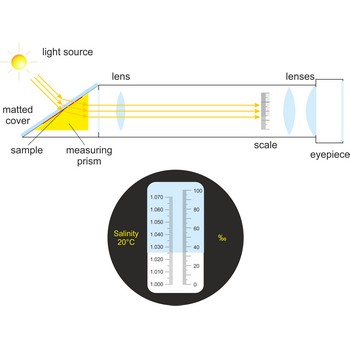
refractometer → refraktometar
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
X-ray diffraction pattern → rendgenski difrakcijski uzorci
X-ray diffraction pattern is an interference pattern created by x-rays as they pass through a solid material. Studying X-ray diffraction patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms.
X-ray spectrum → spektar X-zraka
X-ray spectrum is a set of characteristic X-ray frequencies or wavelengths produced by a substance used as a target in an X-ray tube. Each element has a characteristic X-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number and the frequencies of certain lines in the X-ray spectrum.
resistivity → električna otpornost
Electrical resistivity, or specific resistance (ρ) is the electric field strength divided by the current density when there is no electromotive force in the conductor. Resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material. Materials with low resistivity are good conductors of electricity and materials with high resistivity are good insulators.
For a conductor of uniform cross section with area A and length L, and whose resistance is R, the resistivity is given by
The SI unit is Ω m.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sintetički materijal." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table