white light → bijela svjetlost
White light is a mixture of lights of all colours. If white light is passed through a glass prism or an optical lattice, it is separated into several colours (the visible light spectrum).
Dalton’s atomic theory → Daltonova atomska teorija
Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory of chemical combination, first stated by John Dalton in 1803. It involves the following postulates:
1. Elements consist of indivisible small particles (atoms).
2. All atoms of the same element are identical; different elements have different types of atom.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
4. ’Compound elements’ (i.e. compounds) are formed when atoms of different elements join in simple ratios to form ’compound atoms’ (i.e. molecules).
Dalton also proposed symbols for atoms of different elements (later replaced by the present notation using letters).
decomposition → raspadanje
Decomposition occurs when chemical compounds are broken up into simple molecules, and even as far as their original elements. These processes are normally irreversible. An example of decomposition is when ammonium nitrate is heated. This produces nitrous oxide and water which are unable to recombine.
dissociation → disocijacija
Dissociation is the process by which a chemical combination breaks up into simpler constituents as a result of either added energy (dissociated by heat), or the effect of a solvent on a dissolved polar compound (electrolytic dissociation). It may occur in the gaseous, solid, or liquid state, or in a solution.
An example of dissociation is the reversible reaction of hydrogen iodide at high temperatures
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
electrode of the first kind → elektroda prvog reda
Electrode of the first kind is a simple metal electrode immersed in a solution containing its own ion (e.g., silver immersed in a silver nitrate solution). The equilibrium potential of this electrode is a function of the concentration (more correctly of activity) of the cation of the electrode metal in the solution (see Nernst’s electrode potential equation).
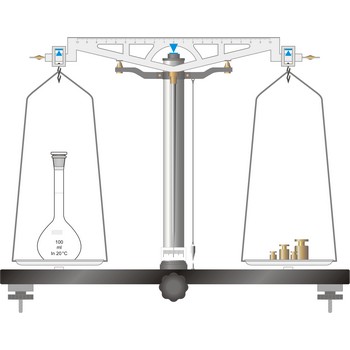
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
Geiger counter → Geigerov brojač
Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller counter) is a device used to detect and measure ionising radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1 000 V is maintained between the electrodes. An ionising particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high potential will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionisations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882-1945). Geiger and W. Muller produced an improved design in 1928.
Gibbs free energy → Gibbsova slobodna energija
Gibbs free energy (G) is an important function in chemical thermodynamics, defined by
where H is the enthalpy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. Gibbs free energy is the energy liberated or absorbed in a reversible process at constant pressure and constant temperature. Sometimes called Gibbs energy and, in older literature, simply free energy.
Changes in Gibbs free energy, ΔG, are useful in indicating the conditions under which a chemical reaction will occur. If ΔG is negative the reaction will proceed spontaneously to equilibrium. In equilibrium position ΔG = 0.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Simple monoclinic lattice." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table