iodine → jod
Iodine was discovered by Bernard Courtois (France) in 1811. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word iodes meaning violet. It is shiny, black, non-metallic solid with characteristic odour. Sublimes easily and as a gas it is violet and intensely irritating to the eyes, nose and throat. Iodine occurs on land and in the sea in sodium and potassium compounds. Required in small amounts by humans. Once used as an antiseptic, but no longer due to its poisonous nature.
ketal → ketal
Ketals are organic compounds formed by addition of an alcohol to a ketone. If one molecule of ketone (RR’CO) reacts with one molecule of alcohol (R"OH) then a hemiketal is formed. The rings of ketose sugars are hemiketals. Further reaction produces a full ketal (RR’C(OR")2). This term, once abandoned, has been reinstated as a subclass of acetals.
luminescence → luminiscencija
Luminescence (from Latin lumen, light) is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (UV, visible or IR) from atoms or molecules as a result of the transition of an electronically excited state to a lower energy state, usually the ground state. Luminescence can be divided into categories by duration (fluorescence or phosphorescence) or by the mechanism that creates the light (radioluminescence, electroluminescence, photoluminescence, thermoluminescence, triboluminescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence). The prefix identifies the energy source responsible for generating or releasing the light.
Phosphorescence is emission of light from a substance exposed to radiation and persisting as an afterglow after the source of excitation has been removed. Fluorescence, on the other hand, is an almost instantaneous effect, ending within about 10-8 second after excitation.
nuclear reactor → nuklearni reaktor
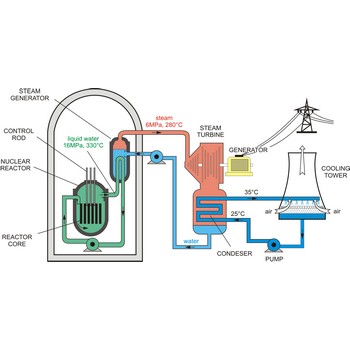
Nuclear reactor is an assembly of fissionable material (uranium-235 or plutonium-239) designed to produce a sustained and controllable chain reaction for the generation of electric power.
The essential components of a nuclear reactor are:
- The core, metal rods containing enough fissionable material to maintain a chain reaction at the necessary power level (as much as 50 t of uranium may be required).
- A source of neutrons to initiate the reaction (such as a mixture of polonium and beryllium)
- A moderator to reduce the energy of fast neutrons for more efficient fission (material such as graphite, beryllium, heavy water, and light water are used)
- A coolant to remove the fission-generated heat (water, sodium, helium, and nitrogen may be used)
- A control system such as rods of boron or cadmium that have high capture cross sections (to absorb neutrons)
- Adequate shielding, remote-control equipment, and appropriate instrumentation are essential for personnel safety and efficient operation.
proline → prolin
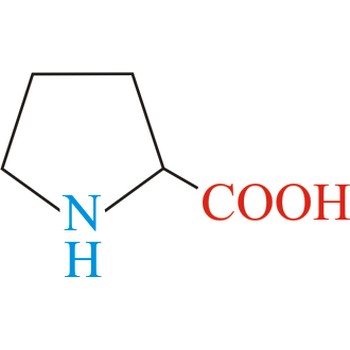
Proline has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive cyclic structure. It is unusual because it is conformationally restricted. The secondary amino (imino) group of proline residues is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing proline. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it.
- Abbreviations: Pro, P
- IUPAC name: pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular weight: 115.13 g/mol
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
styrene → stiren
Styrene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon (C6H5OC2H3O) colourless, toxic liquid with a strong aromatic aroma. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and carbon disulfide, but dissolves only slightly in water. It is used to make plastics such as polystyrene, ABS, styrene-butadiene rubber styrene-butadiene latex and unsaturated polyesters.
threonine → treonin
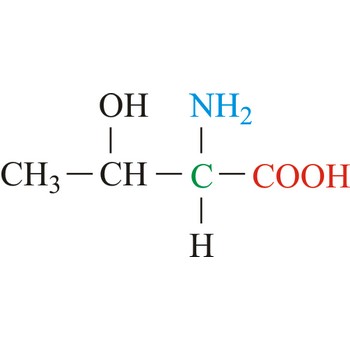
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sekundarni alkohol." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table