solute → otopljena tvar
Solute is a substance that has been dissolved or could be dissolved in another substance (solvent).
mass spectrometry → masena spectrometrija
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which ions are separated according to the mass/charge (m/e) ratio and detected by a suitable detector.
In a mass spectrometer a sample is ionised and the positive ions produced are accelerated into a high-vacuum region containing electric and magnetic fields. These fields deflect and focus the ions onto a detector. A mass spectrum is thus obtained, consisting of a series of peaks of variable intensity to which m/e values can be assigned. Different molecules can be identified by their characteristic pattern of lines.
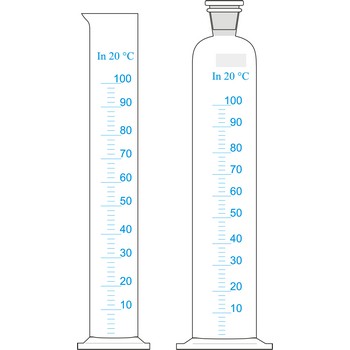
measuring cylinder → menzura
Measuring cylinders (graduated cylinders) are graduated glass cylinders with a capacity from 2 mL to 2 L. They are used when reagent solutions for volume measuring are prepared when accuracy is not of great relevance. The larger the measuring cylinder, the bigger the measuring error.
melting point → talište
Melting point is the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid at normal atmospheric pressure.
A more specific definition of melting point (or freezing point) is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at a specified pressure (normally taken to be atmospheric unless stated otherwise). A pure substance under standard condition of pressure has a single reproducible melting point. The terms melting point and freezing point are often used interchangeably, depending on whether the substance is being heated or cooled.
solvation → solvatacija
Solvation is the process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute ions or molecules.
specific heat → specifični toplinski kapacitet
Specific heat is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius.
specific quantity → specifična veličina
Specific quantity is often convenient to express an extensive quantity (e.g., volume, enthalpy, heat capacity, etc.) as the actual value divided by mass. The resulting quantity is called specific volume, specific enthalpy, etc.
spectroscopy → spektroskopija
Spectroscopy is the analysis of the lines of light emitted from excited atoms as the electrons drop back through their orbitals. These lines give the energy and distances of the electronic orbitals.
spontaneously combustible → samozapaljivi materijal
Spontaneously combustible materials are materials that can ignite without an external source of heat. Heat sufficient to reach the ignition temperature may be generated by reaction with oxygen in the air, by the absorption of moisture, from heat generated during processing, or even from radioactive decay.
stabiliser → stabilizator
Stabiliser is a substance that makes a mixture more stable. Antioxidants and antiozonants are examples of stabilisers; stabilisers are added to paints to prevent the components of the mixture from separating over time.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sửa báo cáo khoản vay nước ngoài." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table