carboxylates → karboksilati
Carboxylates is a common name for all salts that carboxylic acids yield by reacting with hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates and other alkaline reagents.
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
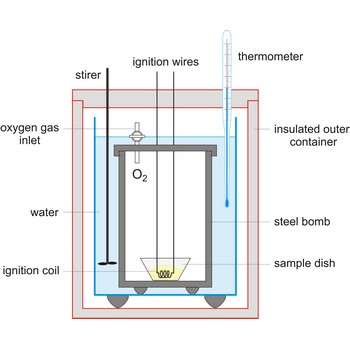
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
carotenoids → karotenoidi
Carotenoids are a group of natural pigments in plants responsible for yellow and orange colours, meltable in fats.
carrier gas → plin nositelj
Carrier gas is the gas, (usually helium or nitrogen), which carries the sample undergoing analysis through the column in gas chromatography.
cation exchange → kationski izmjenjivač
Cation exchange is a cationic resin has positive ions built into its structure and therefore exchanges negative ions. In the cation exchange, the side groups are ionised acidic groups, such as (-SO3H, -COOH, -OH) to which cations H+ are attached. The exchange reaction is one in which different cations in the solution displace the H+ from the solid.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
caesium → cezij
Caesium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1860. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word caesius meaning sky blue or heavenly blue. It is very soft, light grey, ductile metal. Reacts readily with oxygen. Reacts explosively with water. Caesium is found in pollucite [(Cs4Al4Si9O26)·H2O] and as trace in lepidolite. Used as a ’getter’ to remove air traces in vacuum and cathode-ray tubes. Also used in producing photoelectric devices and atomic clocks. Since it ionises readily, it is used as an ion rocket motor propellant.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sửa báo cáo khoản vay nước ngoài." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table