Results 1–9 of 9 for robert de niro - the score lyrics
Bunsen, Robert Wilhem → Bunsen, Robert Wilhem
Robert Wilhem Bunsen (1811-1899) is a German chemist who held professorships at Kassel, Marburg and Heidelberg. His early researches on organometallic compound of arsenic cost him an eye in an explosion. Bunsen's most important work was in developing several techniques used in separating, identifying, and measuring various chemical substances. He also improvement chemical battery for use in isolating quantities of pure metals - Bunsen battery.
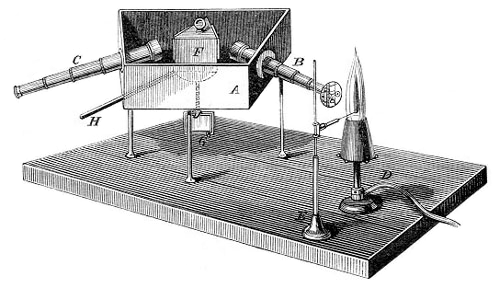
The essential piece of laboratory equipment that has immortalized the name of Bunsen was not invented by him. Bunsen improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the German physicist Gustav Kirchoff and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).
Bunsen burner → Bunsenov plamenik
Bunsen burner is a standard source of heat in the laboratory. German chemist Roberts Bunsen (1811-1899) improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. The Bunsen burner has a vertical metal tube through which a fine jet of fuel gas is directed. Air is drawn in through airholes near the base of the tube and the mixture is ignited and burns at the tube’s upper opening. The flow of this air is controlled by an adjustable collar on the side of the metal tube. When the whole is closed a yellow safety flame is displayed. Where as when the whole is open it displays a power dull blue flame with a faint blue outer flame with a vibrant blue core used u for combustion and hearting. The flame can reach temperatures of 1 500 °C.
Bunsen’s cell → Bunsenov članak
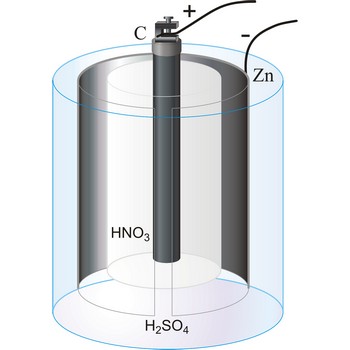
Bunsen’s cell is a primary cell devised by Robert W. Bunsen consisting of a zinc cathode immersed in dilute sulphuric acid and carbon anode immersed in concentrated nitric acid. The electrolytes are separated by a porous pot. The cell gives an e.m.f. of about 1.9 V.
caesium → cezij
Caesium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1860. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word caesius meaning sky blue or heavenly blue. It is very soft, light grey, ductile metal. Reacts readily with oxygen. Reacts explosively with water. Caesium is found in pollucite [(Cs4Al4Si9O26)·H2O] and as trace in lepidolite. Used as a ’getter’ to remove air traces in vacuum and cathode-ray tubes. Also used in producing photoelectric devices and atomic clocks. Since it ionises readily, it is used as an ion rocket motor propellant.
Hirsch funnel → Hirschov lijevak
Hirsch funnels are essentially smaller Büchner funnels and primarily used to collect a desired solid from a relatively small volume of liquid (1-10 mL). The main difference is that the plate is much smaller, while the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical. It is named after the German chemist Robert Hirsch (1856-1913).
Hooke’s law → Hookeov zakon
Hooke’s law stating that the deformation of a body is proportional to the magnitude of the deforming force, provided that the body’s elastic limit (see elasticity) is not exceeded. If the elastic limit is not reached, the body will return to its original size once the force is removed. The law was discovered by English physicist Robert Hooke in 1676.
If a body on elastic spring is displaced from its equilibrium position (i.e. if the spring is stretched or compressed), a restitution force tries to return the body back in its equilibrium position. The magnitude of that force is proportional to the displacement of the body
Where F is the restitutional (elastic) force, x is the displacement of the body and k is the spring constant, which depends on dimensions, shape and material of the spring.
Kirchoff, Gustav → Kirchoff, Gustav
Gustav Kirchoff (1824-1887) was a German physicist who, with the chemist Robert Bunsen (1811-1899), laid the foundations of spectral analysis. He realized that the Fraunhofer lines in the Sun's spectrum were due to light from the photosphere being absorbed at those specific wavelengths by elements in the solar atmosphere. He also found that incandescent solids, liquids, and compressed gases emit a continuous spectrum. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the Bunsen and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).

lawrencium → lawrencij
Lawrencium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Torbjorn Sikkeland, Almon E. Larsh and Robert M. Latimer (USA) in 1961. Named in honour of Ernest O. Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Lawrencium was produced by bombarding a mixture of three isotopes of californium with boron-10 and boron-11 ions. Eight isotopes of lawrencium have been synthesized to date, with the longest-lived being lawrencium-256, which has a half-life of about 30 seconds.
rubidium → rubidij
Rubidium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1861. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word rubidius meaning dark red or deepest red. It is soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Ignites in air. Reacts violently with water or oxidants. Rubidium occurs abundantly, but so widespread that production is limited. Usually obtained from lithium production. Used as a catalyst, photocells and vacuum and cathode-ray tubes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Robert de niro - the score lyrics." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table