acid radical → kiseli radikal
Acid radical is an anion left after removal of hydrogen atoms from an acid.
artificial radioactivity → umjetna radioaktivnost
Artificial radioactivity is a creation, with the help of an accelerator or in the nuclear reactor, of isotopes (radionuclides) which are found in nature because they are unstable and by radioactive conversion they are converted to stable isotopes.
artificial radioactive isotope → umjetni radioaktivni izotop
Artificial radioactive isotopes are formed when an atom is bombed with an accelerator or exposing it to slow moving neutrons in a nuclear reactor. In this way isotopes (radionuclides) are obtained which are non-existent in nature because of their unstability and radioactive transition into stable isotopes. Most important radioactive isotopes are:
Radioactive isotope of cobalt is formed when ordinary metal cobalt is bombed with neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
Radioactive isotope of phosphorus is formed when ordinary phosphorus is bombed with deuterons produced in cyclotron.
radioactive isotope of carbon is formed when a nitrogen is bombed with slow moving neutrons in a nuclear reactor. It is mostly used as a radioactive indicator.
beta radiation → beta zračenje
Streams of beta particles are known as beta ray or beta radiation. Beta rays may cause skin burns and are harmful within the body. A thin sheet of metal can afford protection to the skin.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
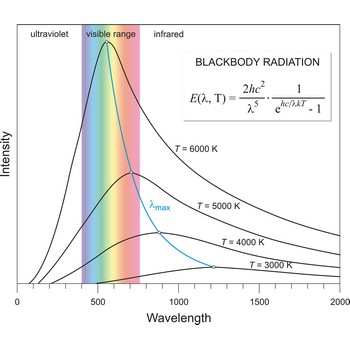
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
electromagnetic radiation spectrum → spektar elektromagnetskog zračenja
Wavelengths of electromagnetic waves can be shown with the help of electromagnetic radiation spectrum. Electromagnetic radiation spectrum is divided into several areas from γ-radiation of very short wavelengths and great energy to radio waves with wavelengths up to 1 000 m. The human eye can only see a narrow part of the electromagnetic spectrum - visible radiation.
free radical → slobodni radikal
Free radical is a molecular fragment having one or more unpaired electrons, usually short-lived and highly reactive. They can be produced by photolysis or pyrolysis in which a bond is broken without forming ions. In formulas, a free radical is conventionally indicated by a dot (·CH3, ·SnH3, ·Cl). Free radicals are known to be formed by ionising radiation and thus play a part in deleterious degradation effects that occur in irradiated tissue. They also act as initiators or intermediates in oxidation, combustion, photolysis, and polymerisation.
microwave radiation → mikrovalna radijacija
Microwave radiation is a electromagnetic radiation with wavelength between 3 mm and 30 cm.
gamma radiation → gama-zračenje
Gamma radiation is electromagnetic radiation of extremely short wavelength. Gamma radiation ranges in energy from about 10-15 J to 10-10 J (10 keV to 10 MeV) (wavelength less than about 1 pm). Gamma rays are emitted by excited atomic nuclei during the process of passing to a lower excitation state.
Gamma rays are extremely penetrating and are absorbed by dense materials like lead and uranium. Exposure to gamma radiation may be lethal.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Radij." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table