hardness → tvrdoća
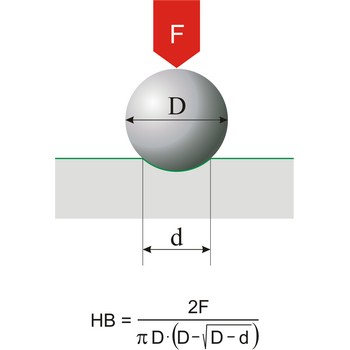
Hardness is the resistance of a material to deformation of an indenter of specific size and shape under a known load. This definition applies to all types of hardness scales except Mohs scale, which is a based on the concept of scratch hardness and is used chiefly for minerals. The most generally used hardness scales are Brinell (for cast iron), Rockwell (for sheet metal and heat-treated steel), Knoop (for metals).
hydration → hidratacija
Hydration is addition of water or the elements of water (i.e. H and OH) to a molecular entity. The term is also used in a more restricted sense for the process:
Rankine cycle → Rankineov ciklus
Rankine cycle is a thermodynamic cycle which can be used to calculate the ideal performance of a heat engine that uses a condensable vapour as the working fluid.
Hesse’s law → Hessov zakon
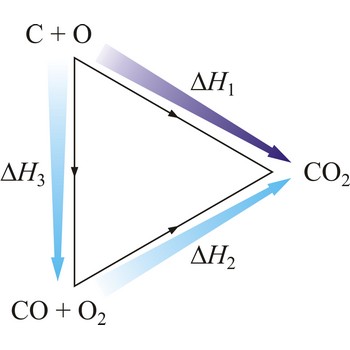
Hesse’s law says that reaction heat of some chemical change does not depend on the way in which the reaction is conducted, but only on starting and ending system state. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. The law was first put forward in 1840 by the Swiss-born Russian chemist Germain Henri Hess (1802-1850).
Hesse’s law can be used to obtain thermodynamic data that cannot be measured directly. For example, it is very difficult to control the oxidation of graphite to give pure CO. However, enthalpy for the oxidation of graphite to CO2 can easily be measured. So can the enthalpy of oxidation of CO to CO2. The application of Hess’s law enables us to estimate the enthalpy of formation of CO.
| C(s) + O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH1 = -393 kJ mol-1 |
| CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH2 = -283 kJ mol-1 |
| C(s) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO(g) | ΔrH3 = -110 kJ mol-1 |
The equation shows the standard enthalpy of formation of CO to be -110 kJ/mol.
ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
specific quantity → specifična veličina
Specific quantity is often convenient to express an extensive quantity (e.g., volume, enthalpy, heat capacity, etc.) as the actual value divided by mass. The resulting quantity is called specific volume, specific enthalpy, etc.
spontaneously combustible → samozapaljivi materijal
Spontaneously combustible materials are materials that can ignite without an external source of heat. Heat sufficient to reach the ignition temperature may be generated by reaction with oxygen in the air, by the absorption of moisture, from heat generated during processing, or even from radioactive decay.
standing wave → stojni val
Standing waves occur when a travelling wave reflects from the fixed ends of a string, producing other waves moving in opposite direction. They are called standing waves because the energy in the string cannot move past the fixed ends, i.e. it stands in the string. In real strings, after some time, standing waves are eventually damped due to friction.
law of conservation of mass → zakon o očuvanju mase
Law of conservation of mass states that no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. The state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction, for example, from a solid to a gas, but its total mass will not change. Note that the energy released (exothermic) or adsorbed (endothermic) in a chemical reaction is a result of energy transfer between atoms and their environment.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Prijenos topline." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table