reversible process → reverzibilan proces
Reversible process or reaction is those that can be reversed by an infinitesimally small change in conditions. For example, ice and water coexist at 101 325 Pa and 0 °C; a very slight temperature increase causes the ice to melt; a tiny temperature decrease causes the water to freeze. Melting or freezing under these conditions can be considered reversible.
seawater → more
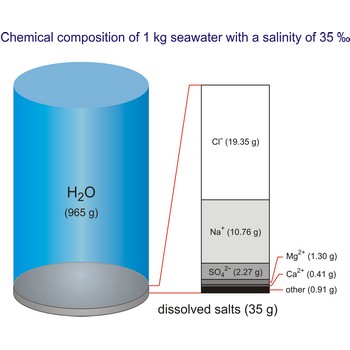
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
state of matter → agregatno stanje
State of matter is one of the tree physical states in which matter can exist, i.e. solid, liquid or gas. Plasma is sometimes regarded as the fourth state of matter. By means of heating a solid substance will cross to liquid state at its melting point. If we heat up a liquid and beyond, at its boiling point it will cross to gaseous state - vapour.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Povišenje vrelišta." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table