bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
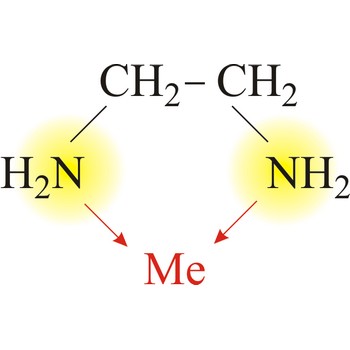
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
electron pair → elektronski par
Electron pair is two electrons within one orbital with opposite spins responsible for a chemical bond.
hydrophilic → hidrofilan
Hydrophilic is having a strong tendency to bind or absorb water, which results in swelling and formation of reversible gels. This property is characteristic of carbohydrates.
borane → borani
Borane is any of the group of compounds of boron and hydrogen (B2H6, B4H10, B5H9, B5H11...), many of which can be prepared by action of acid on magnesium boride (Mg3B2). Boranes are a remarkable group of compounds in that their structures cannot be described using the conventional two-electron covalent bond model.
branched chain → razgranati lanac
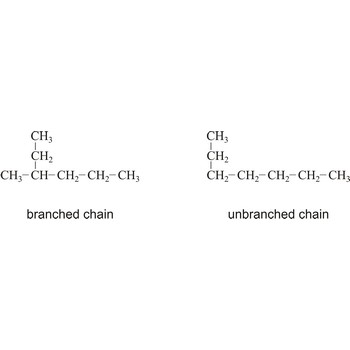
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
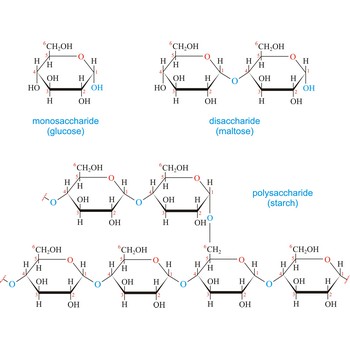
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polarna kovalentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table