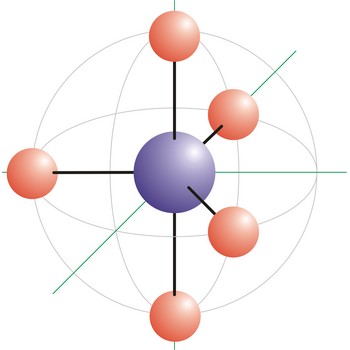
trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry → trigonska bipiramidalna geometrija molekule
Trigonal bipyramidal (trigonal bipyramidal shape) is a molecular geometry that results when there are five bonds and no lone pairs on the central atom in the molecule. Three of the bonds are arranged along the atom’s equator, with 120° angles between them; the other two are placed at the atom’s axis. Axial bonds are at right angles to the equatorial bonds. Molecules with an trigonal bipyramidal electron pair geometries have sp3d (or dsp3) hybridization at the central atom. The PCl5 molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry.
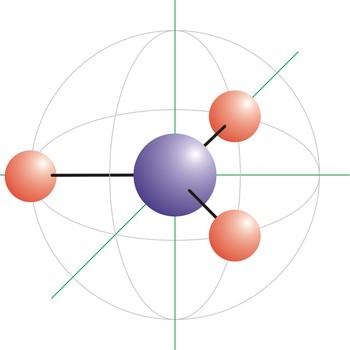
trigonal planar molecular geometry → trigonska planarna geometrija molekule
Trigonal planar is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The pairs are arranged along the central atom’s equator, with 120° angles between them. Molecules with an trigonal planar electron pair geometries have sp2d hybridization at the central atom. The carbonate ion (CO32-) has a trigonal planar geometry.
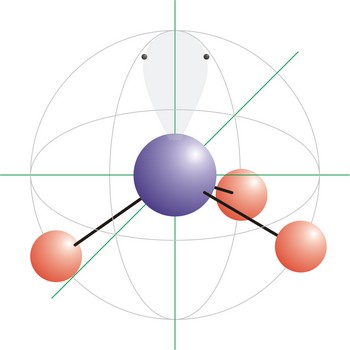
trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry → trigonska piramidalna geometrija molekule
Trigonal pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Molecules with an tetrahedral electron pair geometries have sp3 hybridization at the central atom. Ammonia (NH3) is a trigonal pyramidal molecule.
tryglyceride → triglicerid
Triglyceride is an ester of glycerol and three fatty acids. It is the main constituent of vegetable oil and animal fats. The fatty acids attached to the glycerol can be the same or different. Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals are typically composed only of even numbers of carbon atoms (usually from 16 to 20) due to the way they are bio-synthesized from acetyl CoA.
ultraviolet light → ultraljubičasto svjetlo
Ultraviolet light (UV light or UV radiation) is an electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of x-rays, but shorter than that of visible light. Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage.
unsaturated fatty acid → nezasićena masna kiselina
Unsaturated fatty acid is a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms. Their carbon chain has one or more double or triple valence bond per molecule. The most important of these are:
| Oleic (9-octadecenoic acid) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Linoleic (9,12-octadecadienoic acid) | CH3(CHCH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CHCH2)7COOH |
| Linolenic (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid) | CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CHCH2)7COOH |
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
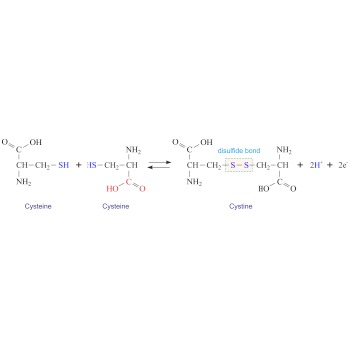
Cystine → Cistin
Cystine (C6H12N2O4S2) is a dimer of cysteine. It is formed by the oxidation of the thiol groups (-SH) of two cysteines generating a disulphide bridge (-S-S-). Cystine is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water. Cystine is particularly abundant in skeletal and connective tissues and in hair, horn, and wool.
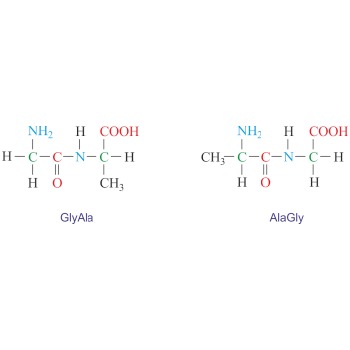
Dipeptide → Dipeptid
Dipeptide is an organic compound formed when two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond. Depending on which groups of amino acids are involved in the peptide bond four dipeptides can be formed from two different amino acids. For example, glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) can give two symmetrical dipeptides (GlyGly and AlaAla) and two unsymmetrical dipeptides (GlyAla and AlaGly). The naming is done by reading the sequence from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polarna kovalentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table