invert sugar → invertni šećer
Invert sugar is a mixture of equal parts of glucose and fructose resulting from the hydrolysis of sucrose (saccharose). The name stemming from the fact that it rotates of plane polarized light in the opposite direction of sucrose. Sucrose is dextrorotatory - it rotates polarized light clockwise ([α]D = +66.5°). Invert sugar rotates the plane of the polarized light counterclockwise ([α]D = -22°) due to the strongly levorotatory nature of fructose ([α]D = -92°).
Homemade artificial honey (invert sugar syrup): Dissolve two parts of household sugar (1 kg) with stirring in one part of water (0.5 kg) in a saucepan over low heat. Add 1 g of citric acid or the juice of one lemon to the mixture. Bring the ingredients to a slow boil. It can take anywhere between 15 minutes to 1 hour. The end result is sticky, golden syrup. Let it sit at room temperature until it is cool.
methionine → metionin
Methionine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of the two sulfur-containing amino acids. Methionine is a fairly hydrophobic amino acid and typically found buried within the interior of a protein. It can form stacking interactions with the aromatic moieties of tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Met, M
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2S
- Molecular weight: 149.21 g/mol
nonpolar molecule → nepolarna molekula
Nonpolar molecule is a molecule which has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are formed. For example, the Cl2 molecule has no polar bonds (molecule with one type of atom), CH4 is a non-polar molecule (due to its symmetry). Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve in water as they cannot form hydrogen bonds (thus are hydrophobic) but do dissolve in lipids or fats (lipophilic).
optical activity → optička aktivnost
Optical activity is the ability of a chiral molecule to rotate the plane of plane-polairzed light. Molecules of an optically active substance cannot be superimposed on their own mirror images, just as your left hand cannot be superimposed on your right when both are held palm-down.
optically active matter → optički aktivna tvar
Optically active matter, by polarized light passing through it, turns the flat of polarized light leftwards or rightwards.
polonium → polonij
Polonium was discovered by Marie Curie (Poland) in 1898. Named for Poland, native country of Marie Curie. It is silvery-grey, extremely rare, radioactive metal. Soluble in dilute acids. Highly toxic. Severe radiotoxicity. Carcinogen. Polonium occurs in pitchblende. Produced by bombarding bismuth with neutrons. Used in industrial equipment that eliminates static electricity caused by such processes as rolling paper, wire and sheet metal.
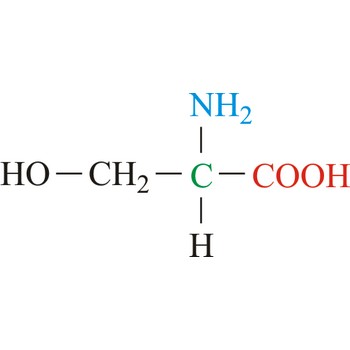
serine → serin
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
thin layer chromatography → tankoslojna kromatografija
Thin layer chromatography. (TLC) is a technique for separating components in a mixture on the basis of their differing polarities. A spot of sample is placed on a flat sheet coated with silica and then carried along by a solvent that soaks the sheet. Different components will move different distances over the surface. TLC is a useful screening technique in clinical chemistry; for example, it can be used to detect the presence of drugs in urine.
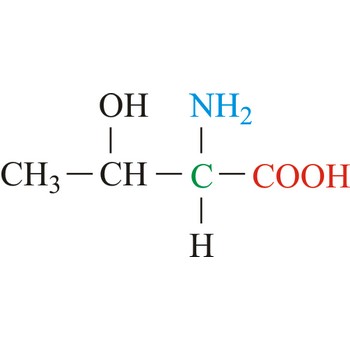
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table