Schrodinger equation → Schrodingerova jednadžba
Schrödinger equation is the basic equation of wave mechanics which, for systems not dependent on time, takes the form:
where Ψ is the wavefunction, V is the potential energy expressed as a function of the spatial coordinates, E its total energy, ![]() 2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
sediment → sediment
1. Sediment is a fragmental material that originates from weathering of rocks and is transported by, suspended in, or deposited by water or air or is accumulated in beds by other natural agencies. When solidified, sediments form sedimentary rocks.
2. Strictly, sediment is a solid material that has settled down from a state of suspension in a liquid.
selenium → selenij
Selenium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word selene meaning moon. It is soft metalloid similar to sulfur. Ranges from grey metallic to red glassy appearance. Unaffected by water. Soluble in alkalis and nitric acid. Burns in air. Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Selenium is obtained from lead, copper and nickel refining. Conducts electricity when struck by light. Light causes it to conduct electricity more easily. It is used in photoelectric cells, TV cameras, xerography machines and as a semiconductor in solar batteries and rectifiers. Also colours glass red.
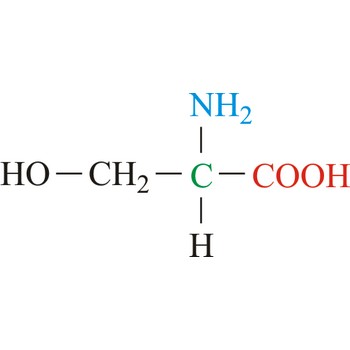
serine → serin
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
significant figures → značajne znamenke
Measurements are not infinitely accurate: we must estimate measurement uncertainty. The number of significant figures is all of the certain digits plus the first uncertain digit.
Rules for significant figures:
- Disregard all initial zeros.
- Disregard all final zeros unless they follow a decimal point.
- All remaining digits including zeros between nonzero digits are significant.
| 0.0023 | has two significant figures |
| 0.109 | has three significant figures |
| 2.00 | has three significant figures |
| 70 | has one significant figure |
In addition and subtraction, the number of significant figures in the answer depends on the original number in the calculation that has the fewest digits to the right of the decimal point.
In multiplication and division, the number of significant figures in a calculated result is determined by the original measurement that has the fewest number of significant digits.
In a logarithm of a number, keep as many digits to the right of the decimal point as there are significant figures in the original number.
In an antilogarithm of a number, keep as many digits as there are digits to the right of the decimal point in the original number.
silver coulometer → srebrni kulometar
Silver coulometer consists of a platinum vessel which acts as a cathode and contains a solution of pure silver nitrate as an electrolyte (c(AgNO3) = 1 mol/L). A rod of pure silver enclosed in a porous pot acts as the anode. The current density at the anode should not exceed 0.2 Acm-2. After electrolysis, the electrolyte is taken out and the platinum vessel is washed, dried and weighed. The increase in the weight gives the amount of silver deposited (96500 C of electricity deposits 107.88 g of silver). From the mass of the silver deposited, the coulomb involved in the reaction can be calculated.
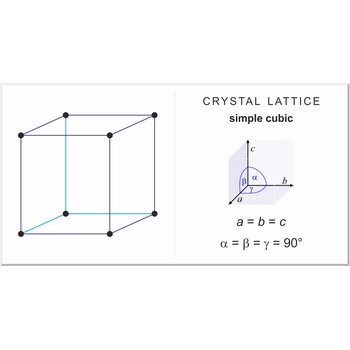
simple cubic lattice → jednostavna kubična rešetka
Simple or primitive cubic lattice (sc or cubic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angels α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the sc structures the spheres fill 52 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is one (8×1/8 = 1). This is only one metal (α-polonium) that have the sc lattice.
simple magnifier → lupa
Simple magnifier is a converging lens, placed between the object and the eye, with the object inside the focal length of the lens. The angular magnification of a simple magnifier is:
where f is the focal length of the lens and 15 cm is the near point distance for a normal eye. The image of the object is virtual, which means that the rays do not actually pass through the point of intersection, that is, it can not be seen on a screen.
sodium → natrij
Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word natrium meaning sodium carbonate. It is soft silvery-white metal. Fresh surfaces oxidize rapidly. Reacts vigorously, even violently with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of melted sodium chloride (salt), borax and cryolite. Metallic sodium is vital in the manufacture of organic compounds. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is table salt. Liquid sodium is used to cool nuclear reactors.
solution composition → sastav otopine
Solutions are homogenous mixtures of several components. The component which is found in a greater quantity is called the solvent and the other components are called solutes. Quantitative composition of a solution can be expressed by concentration (amount, mass, volume and number), by fraction (amount, mass, and volume), ratio (amount, mass, and volume) and by molality. Amount, mass, and volume ratio are numerical, nondimensional units and are frequently expressed as percentage (% = 1/100), promile (‰ = 1/1000) or parts per million (ppm = 1/1 000 000). If it is not defined, it is always related to the mass ratio.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table