gas thermometer → plinski termometar
Gas thermometer is a device for measuring temperature in which the working fluid is a gas.
thermometer → termometar
Thermometers are devices for measuring temperature. Linear and volume thermal expansion are macroscopic properties of matter, which can be easily measured, relative to measurements of microscopic properties, on the basis of which, temperature is defined. Thermometers based on thermal expansion are secondary instruments that is, they have to be calibrated in comparison to a standard thermometer. In a thermometer with liquid, mercury or alcohol is placed in a small glass container. If temperature increases, the liquid undergoes volume expansion and rises in a capillary. The level of the raised liquid is the measure of temperature. Mercury thermometers measure temperatures in the temperature range between -39 °C and 300 °C. Alcohol thermometers measure lower temperatures. Bimetal thermometers have a spiral spring, which consists of two metals with different coefficients of linear expansion. When temperature changes, metals undergo different change in length and the consequence twisting of the spring is transferred to a pointer, the deflection of which is the measure of temperature.
universal gas constant → univerzalna plinska konstanta
Universal gas constant R has the value of 8.314 472(15) J K-1 mol-1. It corresponds to the volume work performed by one mole of gas heated by 1 K at standard pressure.
amount fraction → količinski udio
Amount fraction, xA, (y for gaseous mixtures) is the ratio of the amount of substance (number of moles) of substance A to the total amount of substance in a mixture.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
Boltzmann constant → Boltzmannova konstanta
The Boltzmann constant (k or kB) is the physical constant describing the relationship between the thermodynamic temperature and the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas. It equals the molar gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA and has the value 1.380 648 52(79)×10-23 J/K. It is named after the Austrian physicist Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906).
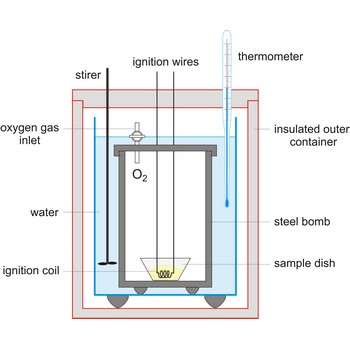
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
carrier gas → plin nositelj
Carrier gas is the gas, (usually helium or nitrogen), which carries the sample undergoing analysis through the column in gas chromatography.
equation of state → jednadžba stanja
Equation of state is an equation relating the pressure, volume, and temperature of a substance or system. Equation of state for ideal gas
where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
partial pressure → parcijalni tlak
Partial pressure is a pressure that one component of gas mixture would have if it were alone in the same volume and at the same temperature as the mixture is in now.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Plinski termometar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table