nuclear magnetic resonance → nuklearna magnetska rezonancija
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a type of radio-frequency spectroscopy based on the magnetic field generated by the spinning of electrically charged atomic nuclei. This nuclear magnetic field is caused to interact with a very large (1 T - 5 T) magnetic field of the instrument magnet. NMR techniques have been applied to studies of electron densities and chemical bonding and have become a fundamental research tool for structure determinations in organic chemistry.
nucleic acid → nukleinska kiselina
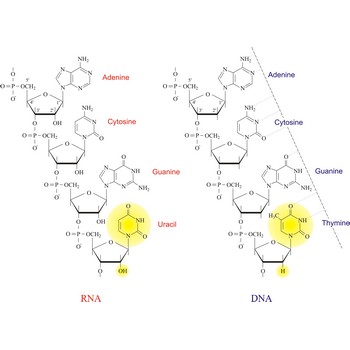
Nucleic acids are a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information. The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Each nucleic acid chain is composed of subunits called nucleotides, each containing a sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. DNA was first discovered in 1869 by the Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895).
Both DNA and RNA contain the two major purine bases adenine (A) and guanine (G) and one of the major pyrimidines, cytosine (C). Of the other two pyrimidines, thymine (T) is found in DNA and uracil (U) is found in RNA. There are two major pentoses in nucleic acids:2'-deoxy-D-ribose in DNA and D-ribose in RNA.
Nucleotides are linked together in both DNA and RNA in a polymeric fashion via covalent bonds. These bonds exist through phosphate-group bridges in which the 5' hydroxyl group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3' hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide. RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule, whereas DNA is usually double-stranded.
ortho position → ortho položaj
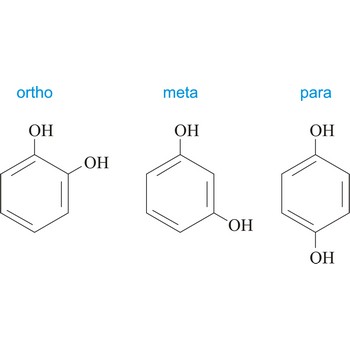
Ortho position in organic chemistry is the one in which there are two same functional groups, tied to a ring of benzene in the positions 1 and 2. The abbreviation o- is used, for example, o-Hydroquinone is 1,2-dihydroxybenzene.
oxo compound → okso-spoj
Oxo compounds are organic compounds that contain the karbonyl group, C=O. The term thus embraces aldehydes, carboxylic acids, ketones, amides, and esters.
para position → para položaj
Para position in organic chemistry is the one in which there are two same functional groups tied to a ring of benzene in the position 1 and 4. The abbreviation p- is used, for example, p-Hydroquinone is 1,4-dihydroxybenzene.
potassium → kalij
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word qali meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word kalium). It is soft, waxy, silver-white metal. Fresh surface has silvery sheen. Quickly forms dull oxide coating on exposure to air. Reacts strongly with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Reacts violently with oxidants. Occurs only in compounds. Potassium is found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3)·6H2O] and sylvite (KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapours in a special retort. Used as potash in making glass and soap. Also as saltpetre, potassium nitrate (KNO3) to make explosives and to colour fireworks in mauve. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissues.
salinity → salinitet
Salinity (S) is a measure of the quantity of dissolved salts in seawater. It is formally defined as the total amount of dissolved solids in seawater in parts per thousand (‰) by weight when all the carbonate has been converted to oxide, the bromide and iodide to chloride, and all organic matter is completely oxidized.
Chlorinity is the oldest of the salinity measures considered and is still a corner-stone in the study of dissolved material in seawater. Based on the principle of constant relative proportions it provides a measure of the total amount of dissolved material in seawater in terms of the concentration of halides. The relationship between chlorinity (Cl) and salinity as set forth in Knudsen’s tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Practical Salinity (SP) was introduced as a replacement for Chlorinity. Practical Salinity is is relatively easy to measure using standard conductometers, measurements are more precise and less time consuming than measurements of Chlorinity and accurate measurements can even be made in situ. Practical salinity SP is defined on the Practical Salinity Scale of 1978 (PSS-78) in terms of the conductivity ratio K15 which is the electrical conductivity of the sample at temperature t68 = 15 °C and pressure equal to one standard atmosphere, divided by the conductivity of a standard potassium chloride (KCl) solution at the same temperature and pressure. The mass fraction of KCl in the standard solution is 0.0324356 (32.4356 g of KCl in 1 kg of solution).
Note that Practical Salinity is a unit-less quantity. Though sometimes convenient, it is technically incorrect to quote Practical Salinity in "psu". For most purposes one can assume that the psu and the ‰, are synonymous.
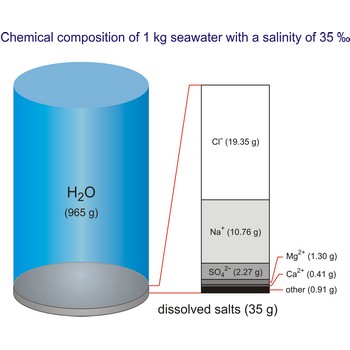
The global average salinity of ocean waters is about 35 ‰, that is, about 35 g of solid substances are dissolved in 1 kg of seawater.
seawater → more
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
sedimentary rocks → sedimentne stijene
Sedimentary Rocks are formed by the accumulation and subsequent consolidation of sediments into various types of rock. There are three major types of sedimentary rocks:
Biogenic sedimentary rocks are formed from organic processes when organisms use materials dissolved in water to build a shell or other skeletal structure.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed directly of the sediments or fragments from other rocks.
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed through evaporation of a chemical rich solution.
Based on their sizes, sediment particles are classified, based on their size, into six general categories:
- boulder (>256 mm)
- cobble (64 - 256 mm)
- gravel (2 - 64 mm)
- sand (1/16 - 2 mm)
- silt (1/256 - 1/16 mm)
- clay (<1/256 mm)
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organski." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table