electroorganic reaction → elektroorganske reakcije
Electroorganic reaction is an organic reaction produced in an electrolytic cell. Electroorganic reactions are used to synthesise compounds that are difficult to produce by conventional techniques. An example of an electroorganic reaction is Kolbe’s method of synthesising alkanes.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
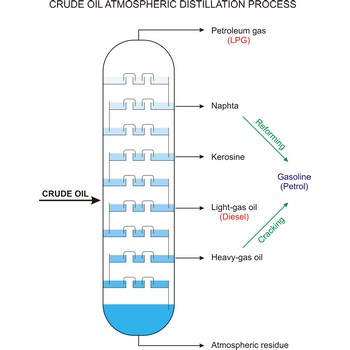
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
Curie → Curie
Maria Sklodowska-Curie (1867-1934) Polish-born French chemist who went to Paris in 1891. She married the physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906) in 1985 and soon began work on seeking radioactive elements other than uranium in pitchblende (to account for its unexpectedly high radioactivity). By 1898 she had discovered radium and polonium although it took her years to purify them. In 1903 the Curies shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Henri Becquerel, who had discovered radioactivity.
elementary substance → elementarna tvar
Elementary substance is a simple and pure substance which can not be, by chemistry methods, decomposed further into simpler substances.
equivalent → ekvivalent
Equivalent (eq) is a unit for describing the amount of a chemical species. In contrast to the mole, the amount of a substance contained in one equivalent can vary from reaction to reaction.
fermentation → fermentacija
Fermentation is a class of biochemical reactions that break down complex organic molecules (such as carbohydrates) into simpler materials (such as ethanol, carbon dioxide, and water). Fermentation reactions are catalyzed by enzymes.
geochemistry → geokemija
Geochemistry is the scientific study of the chemical composition of the Earth. It includes the study of the abundance of the Earth’s elements and their isotopes and the distribution of the elements in environments of the Earth (lithosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organska kemija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table