mercury → živa
Mercury has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word hydrargyrum meaning liquid silver. It is heavy, silver-white metal, liquid at ordinary temperatures. Stable in air and water. Unreactive with alkalis and most acids. Gives off poisonous vapour. Chronic cumulative effects. Mercury only rarely occurs free in nature. The chief ore is cinnabar or mercury sulfide (HgS). Used in thermometers, barometers and batteries. Also used in electrical switches and mercury-vapour lighting products.
meta position → meta položaj
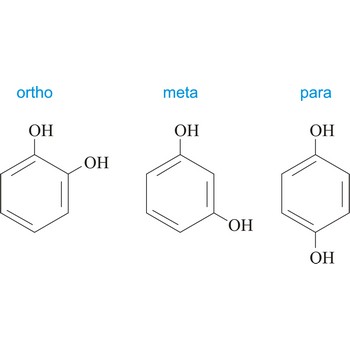
Meta position in organic chemistry is the one in which there are two same functional groups tied to a ring of benzene in position 1 and 3. The abbreviation m- is used, for example, m-Hydroquinone is 1,3-dihydroxybenzene.
methionine → metionin
Methionine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of the two sulfur-containing amino acids. Methionine is a fairly hydrophobic amino acid and typically found buried within the interior of a protein. It can form stacking interactions with the aromatic moieties of tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Met, M
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2S
- Molecular weight: 149.21 g/mol
methyl orange → metil oranž
Methyl orange is an acid-base indicator, in acid it turns red and in a base it turns yellow.
nickel → nikal
Nickel was discovered by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt (Sweden) in 1751. The origin of the name comes from the German word kupfernickel meaning Devil’s copper or St Nicholas’s (Old Nick’s) copper. It is hard, malleable, silvery-white metal. Soluble in acids, resist alkalis. It can be polished to a lustrous finish. Resists corrosion in air under normal conditions. Nickel is chiefly found in pentlandite [(Ni,Fe)9S8] ore. The metal is produced by heating the ore in a blast furnace which replaces the sulfur with oxygen. The oxides are then treated with an acid that reacts with the iron not the nickel. Used in electroplating and metal alloys because of its resistance to corrosion. Also in nickel-cadmium batteries, as a catalyst and for coins.
non-metal → nemetal
Non-metals are defined as elements that are not metals.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are poor conductors.
- They are brittle, not ductile in their solid state.
- They show no metallic lustre.
- They may be transparent or translucent.
- They have low density.
- They form molecules which consists of atoms covalently bonded; the noble gases are monoatomic.
Their chemical properties are generally:
- They usually have four to eight valence electrons.
- They have high electron affinities (except the noble gases)
- They are good oxidising agents (except the noble gases)
- They have hydroxides which are acidic (except the noble gases)
- They are electronegative.
nuclear magnetic resonance → nuklearna magnetska rezonancija
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a type of radio-frequency spectroscopy based on the magnetic field generated by the spinning of electrically charged atomic nuclei. This nuclear magnetic field is caused to interact with a very large (1 T - 5 T) magnetic field of the instrument magnet. NMR techniques have been applied to studies of electron densities and chemical bonding and have become a fundamental research tool for structure determinations in organic chemistry.
nucleotide → nukleotid
Nucleotides are the components that made up nucleic acids. They have three major components: the first component is a nitrogenous base, which is derivative of one of two parent compounds, pyrimidine or purine; the second is a pentose, or five carbon sugar group; the third is a unit of phosphate. Each group of three nucleotides in a gene is known as a codon. Whenever the phosphate group is not present, a nucleotide becomes a nucleoside.
oil of vitriol → vitriolno ulje
Oil of vitriol is an obsolete name for sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Very old way of making sulfuric acid is by heating green vitriol (FeSO4*7H2O) to decomposition and collecting the acid vapors evolved.
ortho position → ortho položaj
Ortho position in organic chemistry is the one in which there are two same functional groups, tied to a ring of benzene in the positions 1 and 2. The abbreviation o- is used, for example, o-Hydroquinone is 1,2-dihydroxybenzene.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organic acid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table