logarithmic scale → logaritamska skala
Logarithmic scale is the one in which values of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, in fact represents values of 1, 10, 100, 1 000, 10 000. Logarithmic scales are often used to simplify graphs and tables, where otherwise changes of data at the lower end of the scale would be difficult to distinguish (e.g. a graph axis which would normally have values from 1 - 1 000 000 is shown by values of 1 - 7). An example of a logarithmic scale is the pH scale.
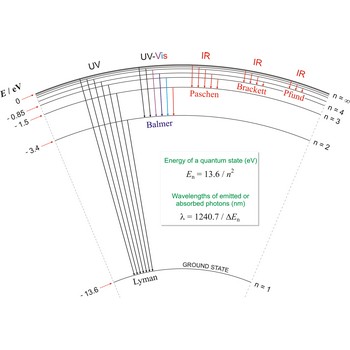
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
melting point → talište
Melting point is the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid at normal atmospheric pressure.
A more specific definition of melting point (or freezing point) is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at a specified pressure (normally taken to be atmospheric unless stated otherwise). A pure substance under standard condition of pressure has a single reproducible melting point. The terms melting point and freezing point are often used interchangeably, depending on whether the substance is being heated or cooled.
Nernst’s division law → Nernstov zakon razdjeljenja
Nernst’s division law states that a substance is divided between two solvents in a way that proportion of concentrations of that substance is at certain temperatures constant, under the condition that both solvents are in the same molecular state. Division coefficient is a proportion of substance concentration in solvents A i B at a defined temperature.
Appearance of division is used for substance extraction.
noble gas → plemeniti plin
Noble gas refers to any element of the group of six elements in group 18 of the periodic table. They are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). Unlike most elements, the noble gases are monoatomic. The atoms have stable configurations of electrons. Therefore, under normal conditions they do not form compounds with other elements.
They were generally called inert gases until about 1962 when xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4, was produced in the laboratory. This was the first report of a stable compound of a noble gas with another single element.
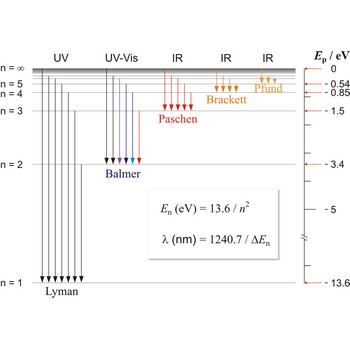
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
phase diagram → fazni dijagram
Phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour-liquid, liquid-solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution.
The figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. The stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the temperature and the pressure. The three phases are in equilibrium at the triple point. The gas and liquid phases are separated by a phase transition only below the temperature of the critical point.
poison → otrov
Poisons are substance, which upon contact or being introduced into an organism, impair or prevent normal metabolic processes from taking place, thus altering the normal functioning of organs or tissues.
Poisons are molecules or material that tends to collect on a catalyst surface, blocking access to active sites or destroying their activities.
Poisons are substance that can reduce a nuclear reaction by absorbing neutrons, thereby preventing more fission. If enough poisons are present in a reactor core, the chain reaction will die out.
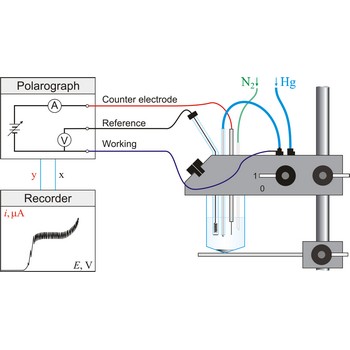
polarography → polarografija
Polarography is a volumetric technique which is based on a diffusion controlled analyte travel to the surface of dropping mercury electrode (DME). The surface of the working electrode (dropping mercury electrode) is constantly renewed under dropping conditions and, thus, the conditions under which reaction takes place are readily reproducible. Depolarisation potential enables identification of ions present in the solution, and by measuring the diffusion current their concentration is calculated. Polarography was discovered in 1922 by the Czech chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský (1890-1967).
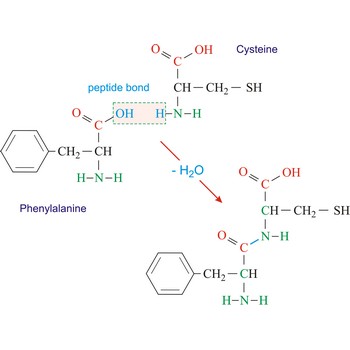
polypeptide → polipeptid
Polypeptides are peptides containing ten or more amino acid residues. The properties of a polypeptide are determined by the type and sequence of its constituent amino acids.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Normalni uvjeti." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table