electrode of the first kind → elektroda prvog reda
Electrode of the first kind is a simple metal electrode immersed in a solution containing its own ion (e.g., silver immersed in a silver nitrate solution). The equilibrium potential of this electrode is a function of the concentration (more correctly of activity) of the cation of the electrode metal in the solution (see Nernst’s electrode potential equation).
Millon’s reaction → Millonova reakcija
Millon’s reaction is used for testing proteins by the appearance of red colour which the proteins give by reacting with a solution of mercury in nitric acid.
molar absorption coefficient → molarni apsorpcijski koeficijent
Molar absorption coefficient (ε) is the absorption coefficient divided by amount-of-substance concentration of the absorbing material in the sample solution (ε = a/c). The SI unit is m2mol-1. Also called extinction coefficient, but usually in units of dm3cm-1mol-1.
Nessler’s reagent → Nesslerov reagens
Nessler’s reagent is a solution of mercury(II) iodide (HgI2) in potassium iodide and potassium hydroxide named after the German chemist Julius Nessler (1827-1905). It is used in testing for ammonia, with which it forms a brown coloration or precipitate.
electrode of the second kind → elektroda drugog reda
Electrodes of the second kind are metal electrodes assembly with the equilibrium potential being a function of the concentration of an anion in the solution. Typical examples are the silver/silver-chloride electrode and the calomel electrode. The potential of the metal is controlled by the concentration of its cation in the solution, but this, in turn, is controlled by the anion concentration in the solution through the solubility product of the slightly soluble metal salt. Contrast with electrode of the first kind and electrode of the third kind.
electrode of the third kind → elektroda trećeg reda
Electrode of the third kind is a metal electrode assembly with the equilibrium potential being a function of the concentration of a cation, other than the cation of the electrode metal, in the solution. The assembly consists of a metal in contact with two slightly soluble salts (one containing the cation of the solid metal, the other the cation to be determined, with both salts having a common anion) immersed in a solution containing a salt of the second metal (e.g., zinc metal--zinc oxalate--calcium oxalate--calcium salt solution). The potential of the metal is controlled by the concentration of its cation in the solution, but this is controlled by the anion concentration in the solution through the solubility product of the slightly soluble metal salt, which, in turn is controlled by the concentration of the cation of the second slightly soluble salt. These electrodes are very sluggish and unstable due to a series of equilibria to be established to produce a stable potential.
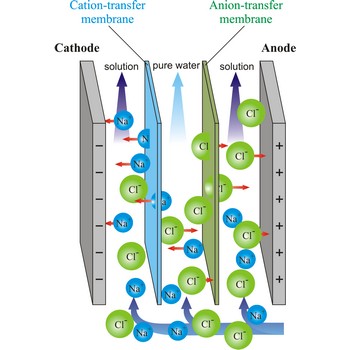
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
neutralisation → neutralizacija
Neutralisation is the process in which an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water.
non-Newtonian fluid → nenewtonski fluid
Non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid whose viscosity changes when the gradient in flow speed changes. Colloidal suspensions and polymer solutions like ketchup and starch/water paste are non-Newtonian fluids.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nezasićena otopina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table